| Electron transfer in the thylakoid membrane generates energy through the synthesis of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). The enzyme ATP synthase catalyzes the formation of ATP from adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and inorganic phosphate (Pi), using the proton gradient established across the membrane. Additionally, NADPH, produced during electron transfer, serves as a source of reducing power for the Calvin cycle, where carbon dioxide is fixed and converted into carbohydrates. This process in the thylakoid membrane plays a crucial role in harnessing light energy and converting it into chemical energy. Agrisera's collection of antibodies to proteins involved in electron transfer offers you the following advantages:
Explore and pick up suitable antibodies here. | 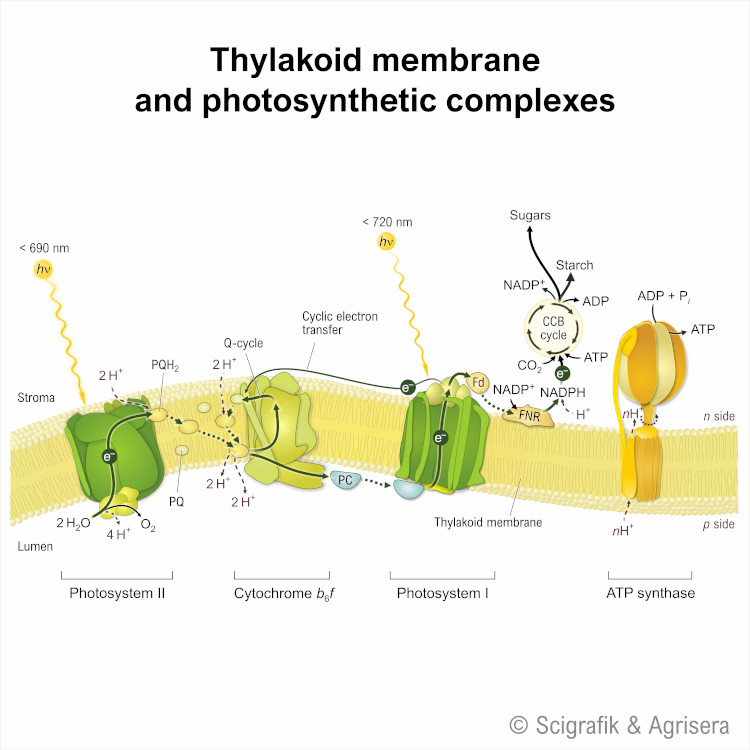 For more images of schemes and photosynthetic complexes, check free images for download here. |
Latest
Interactive workshop focused on antibodies and Western blot held at the University of Wrocław, Poland2025-12-12 Interview with Prof. Debabrata Laha
2025-12-10 Agrisera Prize at Umeå Plant Science Centre 2025
2025-12-05 Interview with Assistant Prof. Ivan Radin
2025-11-27 Agrisera last shipment date in 2025
2025-11-24 Agrisera supports Canadian Society of Plant Biologists Western Regional Meeting
2025-11-21 Agrisera workshop for researchers in China, with Agrisera distributor XMJ
2025-11-21 Western blot workshop with Agrisera exclusive distributor in UK, 2BScientific
2025-11-14 Agrisera at KBC Days 2025
2025-11-12 Interview with Prof. Łucja Kowalewska
2025-11-11
Archive
- December - 2025
- November - 2025
- October - 2025
- September - 2025
- August - 2025
- July - 2025
- June - 2025
- May - 2025
- April - 2025
- March - 2025
- February - 2025
- January - 2025
- December - 2024
- November - 2024
- October - 2024
- September - 2024
- August - 2024
- July - 2024
- June - 2024
- May - 2024
- April - 2024
- March - 2024
- February - 2024
- January - 2024
- December - 2023
- November - 2023
- October - 2023
- September - 2023
- August - 2023
- July - 2023
- June - 2023
- May - 2023
- April - 2023
- March - 2023
- February - 2023
- January - 2023
- December - 2022
- November - 2022
- October - 2022
- September - 2022
- August - 2022
- July - 2022
- June - 2022
- May - 2022
- April - 2022
- March - 2022
- February - 2022
- January - 2022
- December - 2021
- November - 2021
- October - 2021
- September - 2021
- August - 2021
- July - 2021
- June - 2021
- May - 2021
- April - 2021
- March - 2021
- February - 2021
- January - 2021
- December - 2020
- November - 2020
- October - 2020
- September - 2020
- August - 2020
- July - 2020
- June - 2020
- May - 2020
- April - 2020
- March - 2020
- February - 2020
- January - 2020
- December - 2019
- November - 2019
- October - 2019
- September - 2019
- August - 2019
- July - 2019
- June - 2019
- May - 2019
- April - 2019
- March - 2019
- February - 2019
- January - 2019
- December - 2018
- November - 2018
- October - 2018
- September - 2018
- August - 2018
- July - 2018
- June - 2018
- May - 2018
- April - 2018
- March - 2018
- February - 2018
- January - 2018
- December - 2017
- November - 2017
- October - 2017
- September - 2017
- August - 2017
- July - 2017
- June - 2017
- April - 2017
- March - 2017
- February - 2017
- December - 2016
- November - 2016
- October - 2016
- September - 2016
- August - 2016
- July - 2016
- June - 2016
- May - 2016
- April - 2016
- March - 2016
- February - 2016
- January - 2016
- December - 2015
- November - 2015
- October - 2015
- September - 2015
- August - 2015
- July - 2015
- June - 2015
- May - 2015
- March - 2015
- February - 2015
- January - 2015
- December - 2014
- November - 2014
- October - 2014
- September - 2014
- August - 2014
- July - 2014
- June - 2014
- May - 2014
- April - 2014
- March - 2014
- February - 2014
- January - 2014
- December - 2013
- November - 2013
- September - 2013
- August - 2013
- July - 2013
- June - 2013
- May - 2013
- April - 2013
- February - 2013
- January - 2013
- December - 2012
- October - 2012
- September - 2012
- August - 2012
- July - 2012
- June - 2012
- May - 2012
- April - 2012
- March - 2012
- December - 2011
- November - 2011
- September - 2011
- August - 2011
- July - 2011
- April - 2011
- January - 2011
- December - 2010
- October - 2010
- September - 2010
- August - 2010
- July - 2010
- March - 2010
- January - 2010
- December - 2009
- November - 2009
- September - 2009
- July - 2009
- June - 2009
- May - 2009
- March - 2009
- January - 2009
- December - 2008
