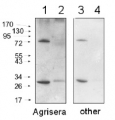
1
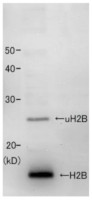
Anti-Histone H2B (Schizosaccharomyces pombe)
AS21 4558 | Clonality: Polyclonal | Host: Rabbit | Reactivity: Schizosaccharomyces pombe
- Product Info
-
Immunogen: Synthetic peptide corresponding to N-terminal Schizosaccharomyces pombe histone H2B, SAAEKKPASKAPAGKA, UniProt: P04913 Host: Rabbit Clonality: Polyclonal
Purity: Serum. Contains 0.05% sodium azide. Format: Liquid Quantity: 50 µl Storage: Store at -20°C; make aliquots to avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. Please remember to spin the tubes briefly prior to opening them to avoid any losses that might occur from material adhering to the cap or sides of the tube. Tested applications: Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP), Western blot (WB) Recommended dilution: 1 : 1000 (WB) Expected | apparent MW: 13.8 | 17, 24-25 kDa (unmodified and mono-ubiquinated H2B) - Reactivity
-
Confirmed reactivity: Schizosaccharomyces pombe Predicted reactivity: Species of your interest not listed? Contact us - Application Examples
-

Crude extract of Schizosaccharomyces pombe was separated on SDS-PAGE and blotted to a membrane using wet transfer. Primary antibody was incubated at 1: 1000, followed by washes and incubation with a secondary goat anti-rabbit IgG HRP conjugated antibodies, used at 1: 10 000 1h/RT. Reaction was developed using chemiluminescence following manufacture's recommendations. Described in Maruyama et al. (2006). - Additional Information
-
Additional information (application): ChIP method for this antibody is described in Maruyama et al. (2006). - Background
-
Background: In the eukaryotic cells, DNA is packaged repetitively into nucleosomes by means of interactions among two molecules of four classes of histone, H2A, H2B, H3 and H4. Each of the histone proteins has an evolutionarily conserved amino-terminal ‘tail’ that protrudes from the nucleosome. This tail is the target of numerous diverse signaling pathways, resulting in the addition of many post-translational modifications. These modifications include phosphorylation, acetylation, methylation, ADP-ribosylation and mono-ubiquitination. Many important new modifications within the structured core and the carboxy-terminal tail regions of histones are also being identified. It is becoming increasingly clear that these modifications represent crucial regulatory events that govern the accessibility and function of the genome. - Product Citations
-
Selected references: Maruyama et al (2006). Histone H2B mutations in inner region affect ubiquitination, centromere function, silencing and chromosome segregation. EMBO J. 2006 Jun 7;25(11):2420-31. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601110. Epub 2006 May 11. PMID: 16688222; PMCID: PMC1478186. - Protocols
-
Agrisera Western Blot protocol and video tutorials
- Reviews:
-
This product doesn't have any reviews.