1
Anti-Sml1 | Suppressor of Mec1 lethality
AS10 847 | Clonality: Polyclonal | Host: Rabbit | Reactivity:Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- Product Info
-
Immunogen: KLH-conjugated synthetic peptide derived from known S.cerevisie Sml1 sequence. Gene ID: 854945
Host: Rabbit Clonality: Polyclonal Purity: Serum Format: Lyophilized Quantity: 50 µl Reconstitution: For reconstitution add 50 µl of sterile water Storage: Store lyophilized/reconstituted at -20°C; once reconstituted make aliquots to avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. Please remember to spin the tubes briefly prior to opening them to avoid any losses that might occur from material adhering to the cap or sides of the tube. Tested applications: Western blot (WB) Recommended dilution: 1 : 1000 (WB) Expected | apparent MW: 11.83 | 11-12 kDa - Reactivity
-
Confirmed reactivity: Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Predicted reactivity: Saccharomyces cerevisiae Not reactive in: No confirmed exceptions from predicted reactivity are currently known - Application Examples
-
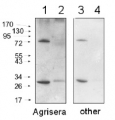
Application example
10 μl total protein from 9.25 x 107 cells of Saccharomyces cerevisiae extracted with 20% TCA as described below were separated on 20% SDS-PAGE and blotted 1.5h (0.5 A) to a nitrocellulose membrane (Whatman PROTRAN BA 85, 0.45 μm). Blots were blocked with 5% non-fat dry milk in TBST for 1.5h at room temperature (RT) with agitation. Blot was incubated in the primary antibody at a dilution of 1: 5 000 overnight at 4C° with agitation. The antibody solution was decanted and the blot was washed 3 times for 10 min in TBST at RT with agitation. Blot was incubated in secondary antibody (anti-rabbit IgG horse radish peroxidase conjugated from Agrisera, (AS09 602) diluted to 1:50 000 for 1h at RT with agitation. The blot was washed as above and developed for 3 min with chemiluminescent detection reagent. Exposure time was 30 seconds.
Courtesy Dr. Andrei Chabes, Umeå University, SwedenApplication examples: 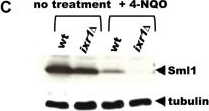
Reactant: Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Yeast)
Application: Western Blotting
Pudmed ID: 21573136
Journal: PLoS Genet
Figure Number: 3C
Published Date: 2011-05-01
First Author: Tsaponina, O., Barsoum, E., et al.
Impact Factor: 5.334
Open PublicationDeletion of IXR1 leads to increased Rnr3 and Rnr4 levels and decreased Sml1 levels.(A) Western blot analysis of Rnr3-HA and Rnr4 levels in wild-type (AC447-2A), ixr1-S366F (TOY619), and ixr1? (TOY621) strains before and after 2 hours treatment with 0.2 mg/L 4-nitroquinoline 1-oxide (4-NQO), 200 mM HU, or 0.02% methyl methanesulfonate (MMS). Rnr3 and Rnr4 levels were quantified in relative units (RU, levels of Rnr3 or Rnr4 divided by the levels of tubulin in corresponding sample) as described in Materials and Methods. ND – not detected. (B) Western blot analysis of Rnr2 levels in wild-type (AC447-2A) and ixr1? (TOY621) strains before treatment and after 2 hours treatment with 0.2 mg/L 4-NQO, 0.02% MMS, or 200 mM HU. (C) Western blot analysis of Sml1 levels in wild-type (W1588-4C) and ixr1? (TOY736) strains before treatment and after 2 hours treatment with 0.02% MMS. (D) Western blot analysis of Rad53 phosphorylation status in wild-type (W1588-4C) and ixr1? (TOY736) strains before treatment and after 2 hours treatment with 0.02% MMS. (E) Deletion of RAD53 but not of SML1 or DUN1 abolishes the upregulation of Rnr3 and Rnr4 levels in ixr1?. Western blot analysis of Rnr3-HA and Rnr4 levels. The following strains were analyzed: wt (AC447-2A), ixr1? (TOY732), ixr1? sml1? (TOY778), ixr1? dun1? sml1? (TOY772), and ixr1? rad53? sml1? (TOY781).
Reactant: Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Yeast)
Application: Western Blotting
Pudmed ID: 23520547
Journal: PLoS One
Figure Number: 6A
Published Date: 2013-03-23
First Author: Azad, G. K., Singh, V., et al.
Impact Factor: 2.942
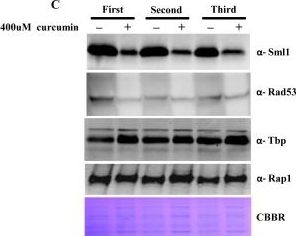
Open PublicationCurcumin induces iron starvation and Sml1p degradation.A & B) RT-PCR Analysis; Logarithmically grown wild-type (1588-4C) cells in standard SC liquid media were treated with either DMSO or curcumin (400 ?M) for 3 hr. Total RNA were extracted and reverse transcribed to cDNA. Semi-quantitative PCR analysis was performed to assess the levels of FRE1, FET3, ACO1, RNR1/2/3/4, HUG1 and ACT1 transcripts. C) Wild-type (1588-4C) cells were cultured up to log phase and treated with either DMSO or curcumin (400 ?M) for 3 hr in triplicate. Whole cell extracts were prepared by TCA extraction method and samples were subjected to western blot anlaysis using antibodies against Sml1, Rad53, Tbp and Rap1. D) Wild-type (1588-4C) cells were grown up to log phase, cultures of cells were divided equally and pre-incubated with either 1 mM PMSF or 100 mM MG132 for 90 min and then treated with curcumin (400 ?M) for 3 hr. In addition, some cells were treated with iron (100 ?M) and rapamycin (50 ng/ml) in presence of curcumin (400 ?M) for 3 hr. Sml1 protein levels were analyzed by western blotting and cellular levels of Rap1, Tbp and Gapdh were used as loading controls.
Reactant: Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Yeast)
Application: Western Blotting
Pudmed ID: 23520547
Journal: PLoS One
Figure Number: 6C
Published Date: 2013-03-23
First Author: Azad, G. K., Singh, V., et al.
Impact Factor: 2.942
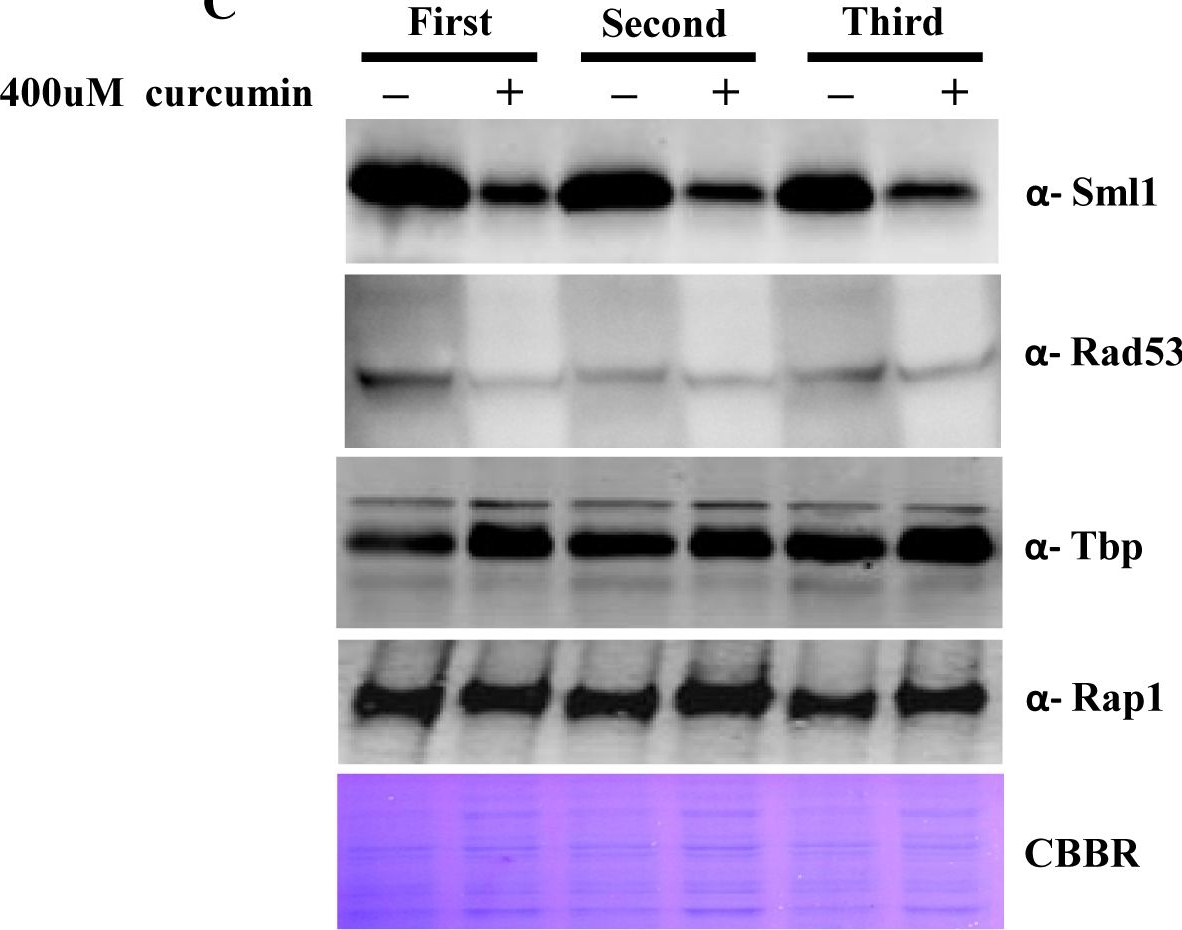
Open PublicationCurcumin induces iron starvation and Sml1p degradation.A & B) RT-PCR Analysis; Logarithmically grown wild-type (1588-4C) cells in standard SC liquid media were treated with either DMSO or curcumin (400 ?M) for 3 hr. Total RNA were extracted and reverse transcribed to cDNA. Semi-quantitative PCR analysis was performed to assess the levels of FRE1, FET3, ACO1, RNR1/2/3/4, HUG1 and ACT1 transcripts. C) Wild-type (1588-4C) cells were cultured up to log phase and treated with either DMSO or curcumin (400 ?M) for 3 hr in triplicate. Whole cell extracts were prepared by TCA extraction method and samples were subjected to western blot anlaysis using antibodies against Sml1, Rad53, Tbp and Rap1. D) Wild-type (1588-4C) cells were grown up to log phase, cultures of cells were divided equally and pre-incubated with either 1 mM PMSF or 100 mM MG132 for 90 min and then treated with curcumin (400 ?M) for 3 hr. In addition, some cells were treated with iron (100 ?M) and rapamycin (50 ng/ml) in presence of curcumin (400 ?M) for 3 hr. Sml1 protein levels were analyzed by western blotting and cellular levels of Rap1, Tbp and Gapdh were used as loading controls.
Reactant: Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Yeast)
Application: Western Blotting
Pudmed ID: 23520547
Journal: PLoS One
Figure Number: 6D
Published Date: 2013-03-23
First Author: Azad, G. K., Singh, V., et al.
Impact Factor: 2.942
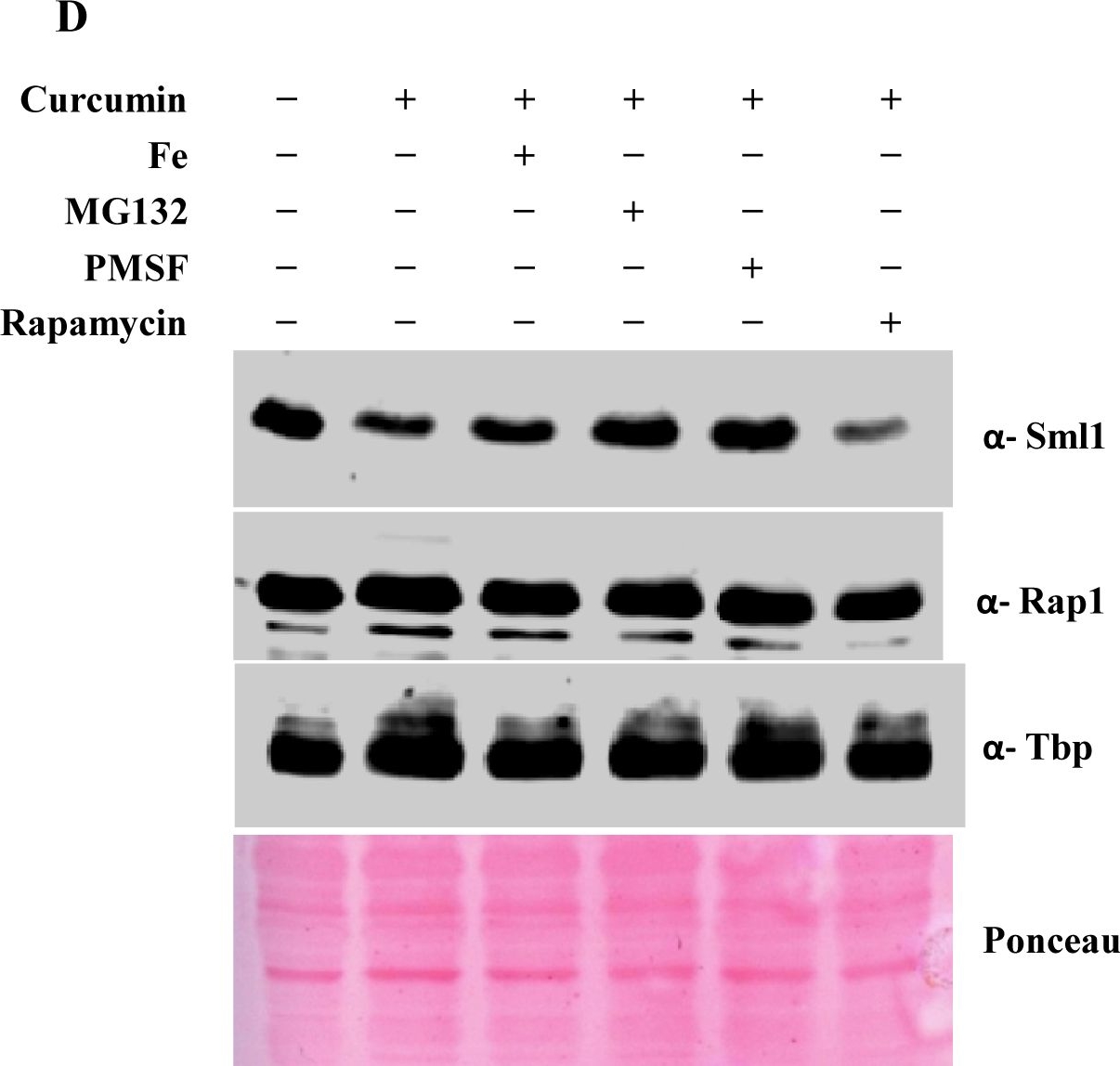
Open PublicationCurcumin induces iron starvation and Sml1p degradation.A & B) RT-PCR Analysis; Logarithmically grown wild-type (1588-4C) cells in standard SC liquid media were treated with either DMSO or curcumin (400 ?M) for 3 hr. Total RNA were extracted and reverse transcribed to cDNA. Semi-quantitative PCR analysis was performed to assess the levels of FRE1, FET3, ACO1, RNR1/2/3/4, HUG1 and ACT1 transcripts. C) Wild-type (1588-4C) cells were cultured up to log phase and treated with either DMSO or curcumin (400 ?M) for 3 hr in triplicate. Whole cell extracts were prepared by TCA extraction method and samples were subjected to western blot anlaysis using antibodies against Sml1, Rad53, Tbp and Rap1. D) Wild-type (1588-4C) cells were grown up to log phase, cultures of cells were divided equally and pre-incubated with either 1 mM PMSF or 100 mM MG132 for 90 min and then treated with curcumin (400 ?M) for 3 hr. In addition, some cells were treated with iron (100 ?M) and rapamycin (50 ng/ml) in presence of curcumin (400 ?M) for 3 hr. Sml1 protein levels were analyzed by western blotting and cellular levels of Rap1, Tbp and Gapdh were used as loading controls.
Reactant: Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Yeast)
Application: Western Blotting
Pudmed ID: 23741394
Journal: PLoS One
Figure Number: 3A
Published Date: 2013-06-07
First Author: Golla, U., Singh, V., et al.
Impact Factor: 2.942
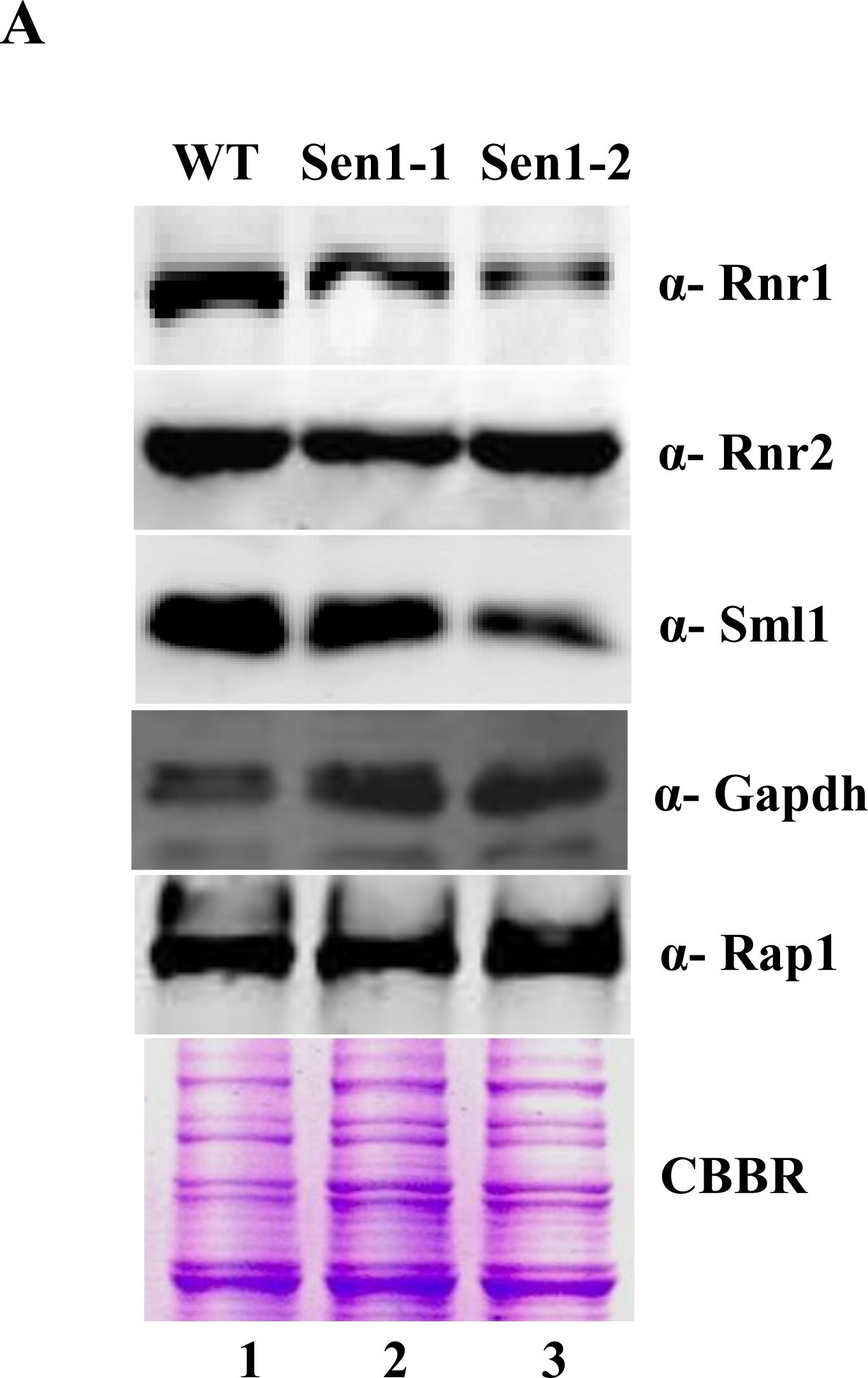
Open PublicationSen1 is required to maintain basal levels of RNR1 through transcription.A) Untreated WT, Sen1-1 and Sen1-2 cells were grown in liquid YPD to mid-log and used for making whole cell protein extracts by TCA precipitation. Samples were analyzed by western blotting with Rnr1, Rnr2, Sml1, Rap1 and Gapdh antibodies. CBBR stands for Coomassie Brilliant Blue R.B) Semi-quantitative analysis of RNR1, HUG1 genes; logarithmically grown Sen1 strains (WT, sen1-1, Sen1-2) in YPD were left untreated for 3 hr. Total RNA was extracted and reverse transcribed to cDNA. Semi-quantitative PCR analysis was performed to assess the levels of RNR1, HUG1 and ACT1 transcripts. The expected sizes of the PCR product for RNR1, HUG1 and ACT1 are 219, 190, and 520 bp respectively. Two repeats of RT-PCR amplifications are shown here.
Reactant: Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Yeast)
Application: Western Blotting
Pudmed ID: 23741394
Journal: PLoS One
Figure Number: 6D
Published Date: 2013-06-07
First Author: Golla, U., Singh, V., et al.
Impact Factor: 2.942
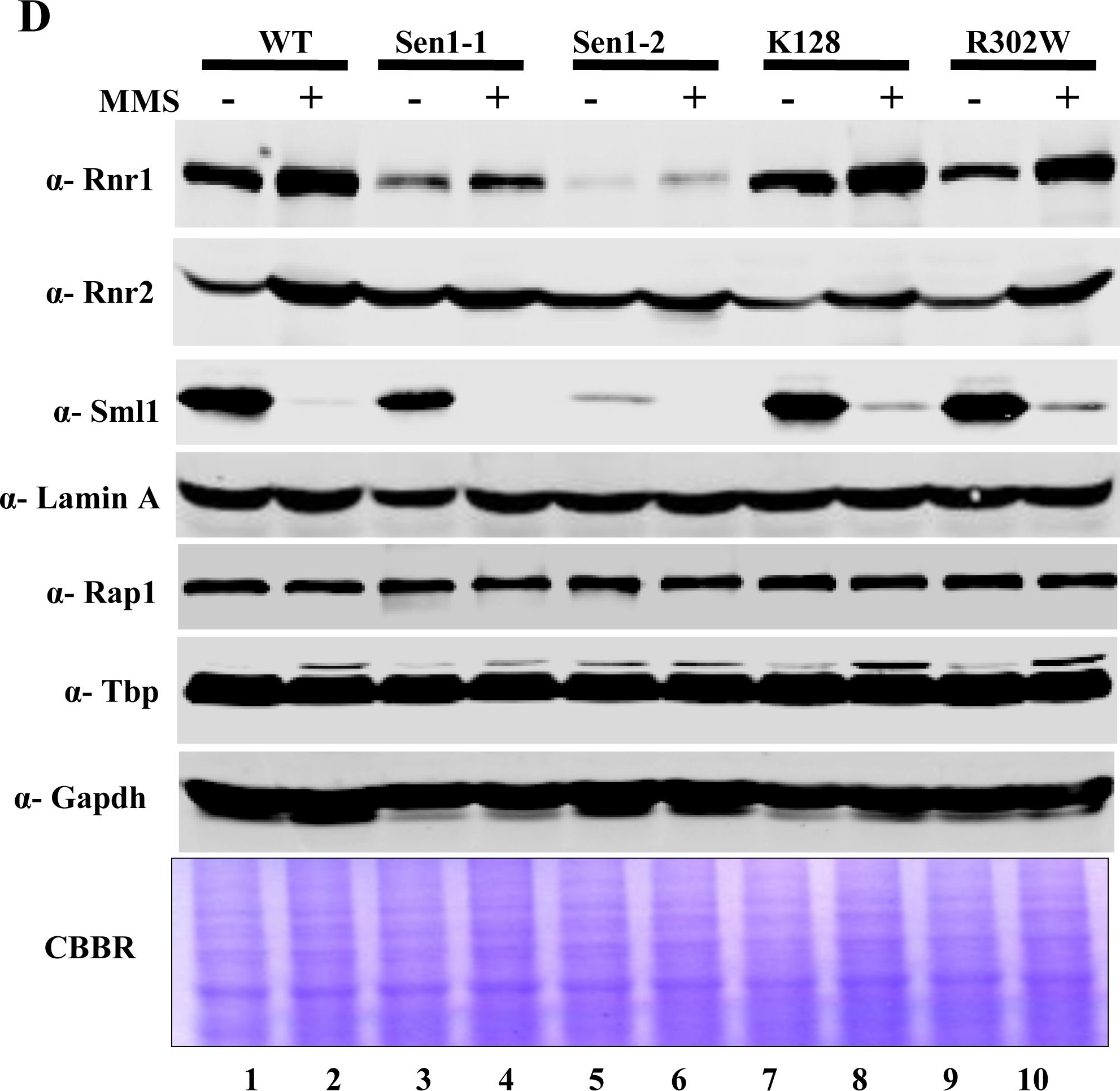
Open PublicationMutations in Sen1p cause sensitivity to DNA damaging agents.A) Growth Assay; Sen1-TAP (Wild-type) and the different mutants of Sen1 [(Sen1(G1747D), Sen1-2(?1-975), Sen1(K128E), Sen1(R302W)] were grown up to log-phase. 3 µl of each undiluted and 10-fold serially diluted cultures were spotted on control YPDA or YPDA plates containing 0.02% MMS, 100 mM HU, 2 mM H2O2 and one set exposed to UV of 100 J/m2. All plates were incubated at 30°C for 3 days and photographed. B) Growth of Sen1 strains was recorded in the presence of different agents like MMS (0.03%), Hydroxy Urea (0.2 M), H2O2 (2 mM) and analyzed in comparison to untreated (control) cells. The average cell density (OD600) of two independent isolates of Sen1 strains with error bars was plotted against different time points (0, 2, 4, 8 and 12 hr). C) Viability Assay; Sen1-TAP (Wt), Sen1-1 and sen1-2 strains were cultured up to mid log phase and treated with 0.03% MMS for 12 hr and cells were stained with 0.3% methylene blue for checking viability. Untreated and heat killed cells were taken as negative and positive controls respectively; viability was observed under light microscope (40X) and photographed. D) MMS (0.03%) treated and untreated Sen1-TAP (WT), Sen1-1, Sen1-2, Sen1(K128E) and Sen1(R302W) cells were used for making whole cell protein extracts by TCA precipitation, samples were analyzed by western blotting. Rnr1, Rnr2, Rnr3 antibodies were used to examine the expression of ribonucleotide reductase proteins and Sml1. E) Quantification of Rnr proteins (Rnr1, 2 & 3) level in Sen1 strains from Fig.4A before and after 3 h of MMS (0.03%) treatment. ‘Lamin A’ was used as the internal control (refer materials and methods). Error bars represent standard error of the mean (SEM).
Reactant: Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Yeast)
Application: Western Blotting
Pudmed ID: 28107343
Journal: PLoS Genet
Figure Number: 4A
Published Date: 2017-01-01
First Author: Dmowski, M., Rudzka, J., et al.
Impact Factor: 5.334
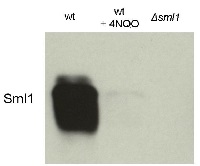
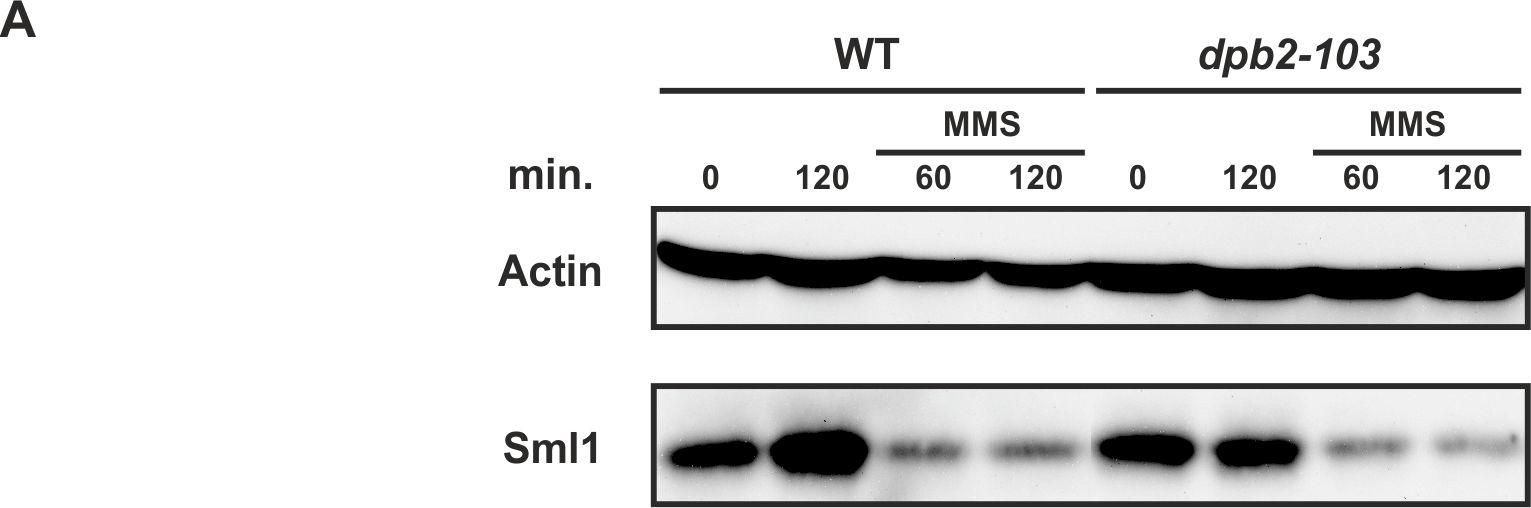
Open PublicationThe Crt1/Dun1 pathway of the replication stress checkpoint is activated in dpb2-103 cells under MMS or HU treatment.(A) Western-Blot detection of Sml1 degradation. Extracts from WT or dpb2-103 yeast cells treated with 0,05% MMS were analyzed. (B) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of RNR3 and HUG1 transcripts in yeast cells released from G1-arrest in YNBD (green) or YNBD with 200 mM HU (red). Transcript levels were analyzed after 120 and 240 minutes of growth and normnalized to wild-type G1-synchronized cells.
- Additional Information
-
Additional information (application): Cell preparation for western blot: cells were harvested by centrifugation (4000 x g , 6 min, 4°C). Supernatant was discarded and cells were resuspended in 500 μl cold TCA buffer (20 mM Tris, pH 8, 50 mM ammonium acetate, 2 mM EDTA, 1 tablet/10 ml of Complete Mini Protease inhibitor cocktail with EDTA (Roche Diagnostics GmbH)). 500 μl 0.5 mm Zirconia/Silica Beads (BioSpec Products, Inc, 11079105z) and 500 μl cold 20% TCA was added. Samples were vigorously vortexed twice for 30 s (kept on ice in between), 750 μl from the liquid phase was transferred into a fresh Eppendorf tube. Samples were centrifuged for 10 min (20000 x g, 4°C). The pellet was resuspended in 300 μl TCA-Laemmli buffer and boiled for 10 min at 100°C. - Background
-
Background: Sml1 is a ribonucleotide reductase inhibitor involved in regulation of dNTP production. It is regulated by Mec1p and Rad53p during DNA damage and S phase. Synonymes: Yml058w.
- Product Citations
-
Selected references: Cerritelli et al. (2020). High density of unrepaired genomic ribonucleotides leads to Topoisomerase 1-mediated severe growth defects in absence of ribonucleotide reductase. Nucleic Acids Res
Corcoles-Saez et al. (2019). Essential Function of Mec1, the Budding Yeast ATM/ATR Checkpoint-Response Kinase, in Protein Homeostasis. Dev Cell. 2018 Aug 20;46(4):495-503.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2018.07.011.
Garbacz et al. (2019). The absence of the catalytic domains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae DNA polymerase ϵ strongly reduces DNA replication fidelity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Jan 30. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz048.
Golla et al. (2017). A systematic assessment of chemical, genetic, and epigenetic factors influencing the activity of anticancer drug KP1019 (FFC14A). Oncotarget. 2017 Sep 30;8(58):98426-98454. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.21416.
Dmowski et al. (2017). Mutations in the Non-Catalytic Subunit Dpb2 of DNA Polymerase Epsilon Affect the Nrm1 Branch of the DNA Replication Checkpoint. PLoS Genet. 2017 Jan 20;13(1):e1006572. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006572.
Mertz et al. (2015). Colon cancer-associated mutator DNA polymerase δ variant causes expansion of dNTP pools increasing its own infidelity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 May 12;112(19):E2467-76. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1422934112. Epub 2015 Mar 31.
Singh et al. (2014). Anti-cancer drug KP1019 modulates epigenetics and induces DNA damage response in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEBS Lett. 2014 Feb 20. pii: S0014-5793(14)00137-9. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2014.02.017.
Azad et al. (2013). Depletion of Cellular Iron by Curcumin Leads to Alteration in Histone Acetylation and Degradation of Sml1p in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. PLoS One, March 8.
Poli et al. (2012).dNTP pools determine fork progression and origin usage under replication stress. The EMBO J. January 2012, 1-12. - Protocols
- Antibody protocols
- Reviews:
-
This product doesn't have any reviews.