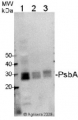
1
Anti-PsbA | D1 protein of PSII, C-terminal (chicken)
AS01 016 | Clonality: Polyclonal | Host: Hen | Reactivity: [global antibody] for higher plants, algae, cyanobacteria and dinoflagellates
Benefits of using this antibody
50% discount on matching standard/positive control
AS01 016S PsbA | D1 protein of PSII positive control/quantitation standard
Use promotional code: Stand50
- Product Info
-
Immunogen: KLH-conjugated synthetic peptide derived from available plant, algal and cyanobacterial PsbA sequences, including Arabidopsis thaliana UniProt: A4QJR4, TAIR: AtCg00020 , Oryza sativa P0C434, Populus alba Q14FH6, Physcomitrella patens Q6YXN7, Chlamydomonas reinhardtii P07753, Synechocystis sp. P14660 and many others
Host: Chicken Clonality: Polyclonal Purity: Purified, total IgY (chicken egg yolk immunoglobulin) in PBS pH 8. Contains 0.02 % sodium azide. Format: Liquid Quantity: 100 µl Storage: Store at 4°C; make aliquots to avoid working with a stock. Please remember to spin the tubes briefly prior to opening them to avoid any losses that might occur from material adhering to the cap or sides of the tube. Tested applications: Western blot (WB) Recommended dilution: 1 :4000-1 : 8000, 5 µg of total protein, (WB) Expected | apparent MW: 38 | 28-30 kDa
- Reactivity
-
Confirmed reactivity: Alaria esculenta, Amphidinium carterae, Anabaena sp., Arabidopsis thaliana, Brachypodium sylvaticum, Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, Chlamydomonas raudensis (both Antarctic and mesophilic strains), Cyanophora sp. , Cyanothece sp. ATCC 51142, Cynara cardunculus, Gonyaulax polyedra, Fucus vesiculosus, Horderum vulgare, Lobaria pulmonaria, Petunia sp., Pinus sylvestris, Spartina alterniflora, Solanum lycopresicum, Synechococcus sp. PCC 7942, Triticum aestivum, Ulva sp., symbiotic dinoflagellates of Stylophora pistillata and Turbinaria reniformis, Zea mays Predicted reactivity: Algae (brown and red), Conifers, Cryptomonads, Legumes, Stramenopiles, Euglenoids, Prochlorophytes, Xantophytes
Species of your interest not listed? Contact usNot reactive in: No confirmed exceptions from predicted reactivity are currently known - Application Examples
-
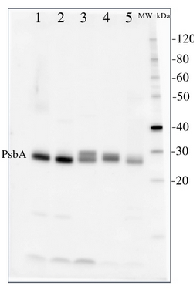
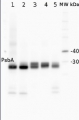
Application example
2 µg of total protein from (1) Arabidopsis thaliana leaf, (2) Horderum vulgare leaf, (3) Chlamydomonas reinhardtii total cell, (4) Synechococcus sp. 7942 total cell, (5) Anabaena sp. total cell extract. All extracts were extracted with PEB (AS08 300) and separated on 4-12% NuPage (Invitrogen) LDS-PAGE and blotted 1h to PVDF. Blots were blocked immediately following transfer for 1h at room temperature with agitation. Blots were incubated in the primary antibody at a dilution of 1: 50 000 for 1h at room temperature with agitation. The antibody solution was decanted and the blot was rinsed briefly twice, then washed once for 15 min and 3 times for 5 min in TBS-T at room temperature with agitation. Blots were incubated in secondary antibody (anti-hen IgY horse radish peroxidase conjugated, recommended secondary antibody AS09 603) diluted to 1:50 000 for 1h/RT with agitation. The blots were washed as above and developed for 5 min with chemiluminescent detection reagent, according the manufacturers instructions. Images of the blots were obtained using a CCD imager (FluorSMax, Bio-Rad) and Quantity One software (Bio-Rad).
Application examples: 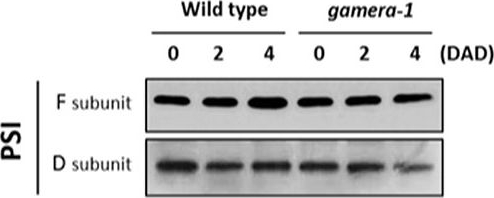
Reactant: Arabidopsis thaliana (Thale cress)
Application: Western Blotting
Pudmed ID: 28791032
Journal: Front Plant Sci
Figure Number: 2A
Published Date: 2017-08-10
First Author: Kohzuma, K., Froehlich, J. E., et al.
Impact Factor: 5.435
Open PublicationChanges in the protein levels of photosynthetic components under extended dark exposure in wild-type and gamera-1. Immunoblot detection of photosynthetic proteins from leaves of Ws and gamera-1 plants incubated after dark adaptation for 0, 2, and 4 days was examined. Specifically, essentially thylakoid fractions were assayed to determine the content of the following proteins: ?-subunit of ATP synthase; the D1 protein, OEC17, OEC23, and OEC33 of PSII; Cyt f and Rieske protein of the cytochrome b6f complex; and the F and D subunits of PSI, after extended dark treatment. Proteins were resolved via SDS-PAGE gel based on equal microgram chlorophyll per lane loading and processed as described in Section “Materials and Methods”. The Large subunit of RuBisco and LHCII stained with either CBB or Ponceau red, respectively, are presented here as loading controls. DAD indicates days after dark adaptation.
- Additional Information
-
Additional information: A number of degradation products may be observed when using anti-PsbA antibodies, including products having apparent molecular weights of 24kDa and 16kDa. D1 degradation is a complex set of events and the products observed can be influenced by both the extraction procedure and the physiology of the cells prior to harvest. Third, cross-linking may occur between D1 and cytochrome b559, shifting the protein higher in the gel. In cyanobacteria (PCC7942), three different bands were competed out by preincubating the antibody with the PsbA free peptide, indicating that all bands are indeed PsbA and its precursors or breakdown products. Competition assays were also performed with spinach and Chlamydomonas, confirming the identity of PsbA bands. Anti-PsbA antibodies will not detect D2 protein, as the peptide used to generate PsbA antibodies has no homology to the D2 sequence.
Example of a simulataneous western blot detection with RbcL, PsbA and PsaC antibodies.Additional information (application): The antibody is appropriate for detecting both, 24 kDa or the 10 kDa C-terminal fragments, whichever is generated under given treatment conditions.In our analysis we have seen both, ca. 24 kDa and ca. 10 kDa fragments from different samples, depending on treatments and isolation procedures.
This antibody will also detect the phosphorylated form of D1as an alternate band to the main band on a high resolution gel.
- Background
-
Background: The PsbA (D1) protein of Photosystem II is rapidly cycled under illumination in all oxygenic photobionts. Disruption of PsbA cycling or losses of PsbA pools are central to photoinhibition of photosynthesis in cyanobacteria, algae and plants under a wide range of conditions including excess light, low temperature and UV exposure. Tracking PsbA pools using the Global PsbA antibody can show the functional content of Photosystem II in a wide range of samples.
- Product Citations
-
Selected references: Rogowski et al. (2023).Enzymatic kinetics of photosystem II with DCBQ as a substrate in extended Michaelis-Menten model. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2023 Oct:247:112780. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2023.112780. Epub 2023 Aug 25.
Vitale et al.(2022) Manipulation of light quality is an effective tool to regulate photosynthetic capacity and fruit antioxidant properties of Solanum lycopersicum L. cv. 'Microtom' in a controlled environment. PeerJ. 2022;10:e13677. Published 2022 Jul 1. doi:10.7717/peerj.13677
Toubiana et al. (2020). Correlation-based Network Analysis Combined With Machine Learning Techniques Highlight the Role of the GABA Shunt in Brachypodium Sylvaticum Freezing Tolerance. Sci Rep , 10 (1), 4489
Sicora et al. (2019). Regulation of PSII function in Cyanothece sp. ATCC 51142 during a light-dark cycle. Photosynth Res. 2019 Mar;139(1-3):461-473. doi: 10.1007/s11120-018-0598-5,
Sevilla et al. (2019). Regulation by FurC in Anabaena links the oxidative stress response to photosynthetic metabolism. Plant Cell Physiol. 2019 May 21. pii: pcz094. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcz094.
Figlioli et al. (2019). Overall plant responses to Cd and Pb metal stress in maize: Growth pattern, ultrastructure, and photosynthetic activity. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2019 Jan;26(2):1781-1790. doi: 10.1007/s11356-018-3743-y.
Krupinska et al. (2019). The nucleoid-associated protein WHIRLY1 is required for the coordinate assembly of plastid and nucleus-encoded proteins during chloroplast development. Planta. 2019 Jan 11. doi: 10.1007/s00425-018-03085-z.
Sicora et al. (2018). Regulation of PSII function in Cyanothece sp. ATCC 51142 during a light–dark cycle. Photosynth Res. 2018 Oct 24. doi: 10.1007/s11120-018-0598-5.
Lentini et al. (2018). Early responses to cadmium exposure in barley plants: effects on biometric and physiological parameters. Acta Physiol Plant (2018) 40: 178. doi: 10.1007/s11738-018-2752-2.
Gonzaga Heredia-Martinez et al. (2018). Chloroplast damage induced by the inhibition of fatty acid synthesis triggers autophagy in Chlamydomonas. Plant Physiol, Sept. 2018.
Kong et al. (2018) Interorganelle Communication: Peroxisomal MALATE DEHYDROGENASE2 Connects Lipid Catabolism to Photosynthesis through Redox Coupling in Chlamydomonas. Plant Cell. 2018 Aug;30(8):1824-1847. doi: 10.1105/tpc.18.00361.
Dy et al. (2018). Galactoglycerolipid Lipase PGD1 Is Involved in Thylakoid Membrane Remodeling in Response to Adverse Environmental Conditions in Chlamydomonas. Plant Cell. 2018 Feb;30(2):447-465. doi: 10.1105/tpc.17.00446.
Kim et al. (2018). The rice zebra3 (z3) mutation disrupts citrate distribution and produces transverse dark-green/green variegation in mature leaves. Rice (N Y). 2018 Jan 5;11(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s12284-017-0196-8.
Yokono et al. (2015). A megacomplex composed of both photosystem reaction centres in higher plants. Nat Commun. 2015 Mar 26;6:6675. doi: 10.1038/ncomms7675.
Su et al. (2014). Exogenous progesterone alleviates heat and high light stress-induced inactivation of photosystem II in wheat by enhancing antioxidant defense and D1 protein stability. Plant Growth Regul DOI 0.1007/s10725-014-9920-1.
Esparza et al. (2013). Katanin Localization Requires Triplet Microtubules in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. PLOS one.
Hoogenboom et al. (2012). Effects of Light, Food Availability and Temperature Stress on the Function of Photosystem II and Photosystem I of Coral Symbionts. POLS one.
Morash et al. (2007). Macromolecular dynamics of the photosynthetic system over a seasonal developmental progression in Spartina alterniflora. Canadian J. of Botany, 2007, 85(5): 476-483, 10.1139/B07-043. - Protocols
-
Agrisera Western Blot protocol and video tutorials
Protocols to work with plant and algal protein extracts
Oxygenic photosynthesis poster by prof. Govindjee and Dr. Shevela
Z-scheme of photosynthetic electron transport by prof. Govindjee and Dr. Björn and Dr. ShevelaPsbA quantitation in plant and algal samples using Agrisera anti-PsbA antibody and PsbA protein standard
Methodology: Plant samples are generally ground with liquid nitrogen in a mortar and pestle. The resulting powder is transferred to a plastic tube. Algal samples can be either concentrated by centrifugation or, preferably, by filtration onto glass fiber filters. Solubilization is performed in Agrisera protein extraction buffer (PEB, AS08 300) containing 0.1mg/mL PefaBloc SC (AEBSF) protease inhibitor (Roche). Disruption is most optimally obtained through flash freezing of the sample in liquid nitrogen alternated with thawing by sonication with a microtip. This process can be repeated depending on the toughness of the sample. The sample is adjusted to 50 mM dithiothreitol and heated to 70°C for 5 minutes. Samples are cooled and centrifuged briefly prior to electrophoresis.
Optimal quantitation is achieved using moderate sample loads per gel lane, generally 0.5 to 2.5 ug total protein, depending on the abundance of the target protein.
Electrophoresis and Immunoblotting: Once solubilized, the proteins can be separated electrophoretically in a number of systems. We obtain optimal results with the Invitrogen NuPAGE gel system using Bis-Tris 4-12% gradient gels. Proteins are separated in MES SDS running buffer according to the manufacturer’s recommendations at 200 V for 35 minutes. The gels are transferred to PVDF in the same apparatus, the SureLock XCell blot module, for 60 minutes at 30 V for a single gel or 80 minutes for a pair. Following transfer the blots are blocked with non-fat dry milk up to 10 % in TBS-T, for 1 h/RT with gentle agitation. The blot is incubated with primary antibody, usually at 1:25 000 to 1:50 000, for 1 h/RT (if extreme femtogram detection reagents are used) or in lower primary antibody dilution for less sensitivie reagents (mid picogram and lower).
For quantitation a relatively high primary antibody: target protein ratio gives more reliable results than immunoblots at low ratios of primary antibody:target protein.
The blot is washed extensively in TBS-T (twice briefly, once for 15 minutes and three times for five minutes). The blot is incubated with secondary antibody, for example goat anti-chicken IgY horse radish peroxidase conjugated, AS09 602 (Agrisera), for 1h/RT. The blot is washed as above and developed with ECL detection reagents.Quantitation: When quantitated standards are included on the blot, the samples can be quantitated using the available software. Excellent quantitation can be obtained with images captured on the Bio-Rad Fluor-S-Max or equivalent instrument using Bio-Rad QuantityOne software. The contour tool is used to select the area for quantitation and the values are background subtracted to give an adjusted volume in counts for each standard and sample. Using above protocol linear standard curves are generated over 1-1.5 orders of magnitude range in target load. It is important to note that immunodetections usually show a strongly sigmoidal signal to load response curve, with a region of trace detection of low loads, a pseudolinear range and a region of saturated response with high loads. For immunoquantitation it is critical that the target proteins in the samples and the standard curve fall within the pseudolinear range. Our total detection range using this protocol spans over 2 orders of magnitude, but the quantifiable range is narrower.
Recommended secondary antibody from Agrisera: Rabbit anti-chicken HRP conjugated or Goat anti-chicken HRP conjugated or Goat anti-chicken ALP conjugated
Recommended chemiluminescent detection reagent: AgriseraECLBright
References:MacKenzie et al (2005). Large reallocations of carbon, nitrogen and photosynthetic reductant among phycobilisomes, photosystems and Rubisco during light acclimation in Synechococcus elongatus are constrained in cells under low environmental inorganic carbon. Arch of Microbiol. 183: 190 - 202.
Bouchard et al. (2006) UVB effects on the photosystem II-D1 protein of phytoplankton and natural phytoplankton communities. Photochem and Photobiol 82: 936-951.Western Blot using IgY
Important note: Please, be aware, that often protocols used for IgG antibodies (rabbit, goat, mice) have to be optimised to get best results with IgY antibodies.1. Block unspecific binding by washing membrane in 25 ml blocking buffer/13x13 cm filer for 2 hours at room temperature on a shaker.
* Example of a Blocking buffer (Blotto)
1x TBS (20 mM Tris/HCl, pH 7.5,150 mM NaCl, 3-5 % low-fat dried milk powder, 0.05 % Tween-20 (or Nonidet P-40)
Blotto - Limitations:
o Usually very effective however: there are complex carbohydrates in milk and these will absorb out antibodies that recognize carbohydrate determinants.
o Some IgY antibodies might recognize milk proteins (high background signal).
o 10 % nonfat dry milk might block so efficiently, and in some cases so well, that no bands of interest will be seen.
Blocking insufficient - alternatives to try:Increase non-fat milk to 10-15 % 1h/RT incubation.
2. Wash each filter briefly, twice, then 1 x 15 minutes and 4 x 5 minutes at RT in Washing buffer. In case of still high background siganl - increase the length of a washing step even more than what is recommended above.
o Washing buffer:
1 x TBS, 0.05 % Tween-203. Add primary antibody to 10-20 ml of Antibody buffer (dilution range from 1:100 to 1: 30 000) and incubate the filter for 1-3 hours at room temperature (or 37°C, optional).
o Antibody buffer: 1 x TBS, 2% milk powder, 0.05 % Tween 204. Rinse the filter briefly twice, following by 1 x 15 and 4 x 5 minutes at RT in Washing buffer.
5. Add secondary antibody in Antibody Buffer. Use for instance rabbit or goat anti-IgY HRP conjugated. Start with the dilution at least 1 :10 000 (even higher dilutions are recommended).
Cross-reactivity signal coming from a secondary antibody can be easily checked by omitting a primary antibody in the whole procedure. Recommended secondary antibody from Agrisera: Rabbit anti-chicken HRP conjugated or Goat anti-chicken HRP conjugated or Goat anti-chicken ALP conjugated6. Wash the filter 4 x 5 minutes in Washing buffer, followed by 1 x 15 minutes in dH2O at room temperature.
Important!
or contact Agrisera Technical Support or talk with us directly on the website (bottom right corner).
Amount of membrane washes. In case of high unspecific background, increase the time of the wash with frequent exchange of Washing buffer.
In case of high background levels, firstly test if the secondary antibody is not contributing to the background. Use a small piece of empty transfer membrane, follow the procedure above without the step with primary antibodies. Recommended chemiluminescence detection reagent in mid picogram range: AgriseraECLBright, since primary antibodies can be used in a very high dilution, often background signal will be diluted out at that step.
Using extra sensitivite development systems (above extreme femtogram) can contribute to increased background signals.
Check also: Western Blot troubleshooting
- Reviews:
-
| 2011-06-30Almost same to upstairs. This antibody works all well in Arabidopsis, tobacco and some other plants. Its activity is really high, but the concentration and the sample load should be optimized depend on different plant materials.Ryouichi Tanaka@Hokkaido University | 2008-12-04This antibody is sufficiently strong and specific, but in western blotting experiments, the concentrations of both the antibody and the samples should be optimized to eliminate non-specific signals. In our laboratory, the antibody is diluted by 10,000 to 20,000 times to detect the D1 protein from leaf extracts of Arabidopsis. It gives a clear signal around 31-32 kD.
Accessories
AS01 016S | Positive control/quantitation standard
50% discount until June 30
Use promotional code: Stand50
AS05 084 | Clonality: Polyclonal | Host: Rabbit | Reactivity: [global antibody] for higher plants, algae, liverwort, cyanobacteria, diatoms | cellular [compartment marker] of thylakoid membrane
Benefits of using this antibody