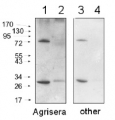
1

Anti-H3K4me3 | Histone H3, trimethylated lysine 4 (H3K4me3)
- Product Info
-
Immunogen: KLH-conjugated synthetic peptide Host: Rabbit Clonality: Polyclonal Purity: Antigen affinity purified Format: Liquid Quantity: 50 µg Storage: Store lyophilized/reconstituted at -20°C; once reconstituted make aliquots to avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. Please remember to spin the tubes briefly prior to opening them to avoid any losses that might occur from material adhering to the cap or sides of the tube. Tested applications: Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Sequencing (ChIP-seq), Dot blot (Dot), ELISA (ELISA), Immunofluorescence (IF), peptide array (PA), Western blot (WB) Recommended dilution: 1-5 µg/IP (ChIP-seq), 1 : 10 000 (Dot), 1 : 100 (ELISA), 1 : 200 (IF), 1 : 2000 (PA), 1 : 1000 (WB) - Reactivity
-
Confirmed reactivity: Human, Solanum lycopersicum Predicted reactivity: Arabidopsis thaliana, Mouse, Oryza sativa, Populus sp., Zea mays
Species of your interest not listed? Contact usNot reactive in: No confirmed exceptions from predicted reactivity are currently known - Application Examples
-
application example 
ChIP assays were performed using human HeLa cells, the antibody against H3K4me3 and optimized PCR primer pairs for qPCR. ChIP was performed with the “Auto Histone ChIP-seq” kit, using sheared chromatin from 1 million cells. A titration consisting of 1, 2, 5 and 10 μg of antibody per ChIP experiment was analyzed. IgG (2 μg/IP) was used as a negative IP control. Quantitative PCR was performed with primers specific for the promoter of the active genes GAPDH and EIF4A2, used as positive controls, and for exon 2 of the inactive myoglobin (MB) gene and the Sat2 satellite repeat, used as negative controls. Figure 1 shows the recovery, expressed as a % of input (the relative amount of immunoprecipitated DNA compared to input DNA after qPCR analysis). These results are in accordance with the observation that trimethylation of K4 at histone H3 is associated with the promoters of active genes.
ChIP-seq was performed on sheared chromatin from 1 million HeLaS3 cells using 1 μg of the anti-H3K4me3 antibodies as described above. The IP’d DNA was subsequently analysed on an Illumina Genome Analyzer. Library preparation, cluster generation and sequencing were performed according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The 36 bp tags were aligned to the human genome using the ELAND algorithm. Image shows the peak distribution along the complete sequence and a 600 kb region of the X-chromosome (A and B) and in two regions surrounding the GAPDH and EIF4A2 positive control genes, respectively (C and D). These results clearly show an enrichment of the H3K4 trimethylation at the promoters of active genes.
Immunofluorescence: human osteosarcoma (U2OS) cells were stained using anti-H3K4me3 antibodies and with DAPI. Cells were fixed with 4% formaldehyde for 20’ and blocked with PBS/TX-100 containing 5% normal goat serum. The cells were immunofluorescently labeled with the H3K4me3 antibody (left) diluted 1:200 in blocking solution followed by an anti-rabbit antibody conjugated to Alexa568 or with DAPI (right), which specifically labels DNA.
Peptide array: the specificity of this antibody was demonstrated by peptide array analyses on an array containing 384 peptides with different combinations of modifications from histone H3, H4, H2A and H2B. The antibody was used at a dilution of 1:2 000.This figure shows a high specificity for the peptides containing the H3K4me3 modification.
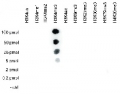
Dot blot: to test the cross reactivity of anti-H3K4me3 antibodies, a Dot Blot analysis was performed with peptides containing other histone modifications and the unmodified H3K4. One hundred to 0.2 pmol of the respective peptides were spotted on a membrane. The antibody was used at a dilution of 1:10 000. This figure shows a high specificity of the antibody for the modification of interest.
ChIP: Arabidopsis thaliana (Col-0) seedlings 14 days after germination using our premium anti-H3K4me3 ChIP-seq grade antibody and rabbit IgG. Error bars represent the standard deviation of at least 3 biological repetitions. 1 μg of H3K4me3 antibody and 1 μg of the negative IgG control were used per ChIP reaction. Quantitative PCR was performed with the positive control FLC-ATG and the negative control FLC-Intron1 primer sets from the kit. The recovery is expressed as % of input. - Additional Information
-
Additional information: Antibody is provided in PBS containing 0,05% azide and 0,05% ProClin 300 at concentration of 1.3 µg/µl. - Background
-
Background: Histones are the main constituents of the protein part of chromosomes of eukaryotic cells. They are rich in the amino acids arginine and lysine and have been greatly conserved during evolution. Histones pack the DNA into tight masses of chromatin. Two core histones of each class H2A, H2B, H3 and H4 assemble and are wrapped by 146 base pairs of DNA to form one octameric nucleosome. Histone tails undergo numerous post-translational modifications, which either directly or indirectly alter chromatin structure to facilitate transcriptional activation or repression or other nuclear processes. Methylation of histone H3K4 is associated with activation of gene transcription. - Product Citations
-
Selected references: Song et al.(2024). Whole-genome landscape of histone H3K4me3 modification during sperm cell lineage development in tomato. BMC Plant Biol. 2024 Jun 27;24(1):610. doi: 10.1186/s12870-024-05318-8.
Mursalimov et al. (2019). Cytological Techniques to Study Cytomixis in Plant Male Meiosis. Methods Mol Biol. 2020;2061:117-129. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-9818-0_9.
Liu et al. (2018). Transcriptomics analyses reveal the molecular roadmap and long noncoding RNA landscape of sperm cell lineage development. Plant J. 2018 Jul 26. doi: 10.1111/tpj.14041. - Reviews:
-
This product doesn't have any reviews.