1
Anti-GLN1 GLN2 | GS1 GS2 glutamine synthetase global antibody
AS08 295 | Clonality: Polyclonal | Host: Rabbit | Reactivity: [global antibody] | Arabidopsis thaliana, Eragrostis tef, Gracilaria gracilis (red algae), Gracilaria lemaneiformis, Leptodictyum riparium (Hedw.) Warnst (moss), Medicago truncatula, Physcomitrella patens, Pinus strobus, Spinacia oleracea, Solanum lycopersicum, Triticum aestivum, Zea mays
Benefits of using this antibody
- Product Info
-
Immunogen: KLH-conjugated synthetic peptide derived from a wide range of available sequences including all isoforms of Arabidopsis thaliana GLN1-1, 1-2, 1-3 and 1-4, (At5g37600, At1g66200, At3g17820, At5g16570)
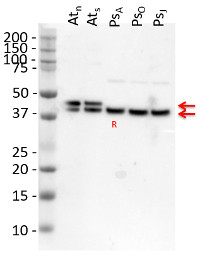
Host: Rabbit Clonality: Polyclonal Purity: Serum Format: Lyophilized Quantity: 50 µl Reconstitution: For reconstitution add 50 µl of sterile water Storage: Store lyophilized/reconstituted at -20°C; once reconstituted make aliquots to avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. Please remember to spin the tubes briefly prior to opening them to avoid any losses that might occur from material adhering to the cap or sides of the tube. Tested applications: Western blot (WB) Recommended dilution: 1 : 10 000 (WB) Expected | apparent MW: 39-40 kDa (GLN1,cytoplasmic form), 44-45 kDa (GLN2, chloroplastic form)
- Reactivity
-
Confirmed reactivity: Arabidopsis thaliana, Eragrostis tef, Gracilaria gracilis (red algae), Gracilaria lemaneiformis, Leptodictyum riparium (Hedw.) Warnst (moss), Medicago truncatula, Physcomitrium patens, Pinus strobus, Spinacia oleracea, Solanum lycopersicum, Triticum aestivum, Zea mays Predicted reactivity: Brachypodium distachyon, Brassica napus, Camellia sinensis, Citrus clementina, Cucumis melo, Daphnia magna, Datisca glomerata, Emiliania huxleyi, Eucalyptus grandis, Gazania splendens, Genlisea aurea, Glycine max, Helianthus annuus, Hordeum vulgare, Lemna minor, Oryza sativa, Panax quinquefolius, Phaseolus angularis, Phytophthora cinnamomi, Populus trichocarpa, Saccharum officinarum, Securigera parviflora, Solanum lycopersicum, Solanum tuberosum, Stevia rebaudiana, Theobroma cacao, Zea mays, Vitis labrusca
GLN1 dicots including: Brassica napus, Phaseolus vulgaris, monocots including: Hordeum vulgare, Oryza sativa, trees: Pinus sylvestris, Populus sp., Zosteria marina
GLN2 dicots including: Brassica napus, Glycine max, Phaseolus vulgaris, monocots including: Triticum aestivum, Oryza sativa
GLN3: Zea maysGLN1 in algae: Chlamydomonas reinhardii
Species of your interest not listed? Contact usNot reactive in: No confirmed exceptions from predicted reactivity are currently known - Application Examples
-
Application example 
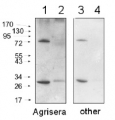
10 µg of total protein extracted freshly from Arabidopsis thaliana wt leaf tissue (Atn non-senescent leaves), Arabidopsis thaliana wt leaf tissue (Ats senescent leaves), Pinus strobus needle tissue (PSA-J) with 1 M Tris-HCl, pH 6.8, 10 % SDS, 15 % sucrose, 0.5 DTT and denatured at 75°C for 5 min. were separated on 10 % Bis-Tris Nupage Novex gel (120 V/45 min. using MES buffer system) and blotted 30 min. to PVDF. Blot was blocked with 5 % non-fat milk 45 min./RT with agitation. Blot was incubated in the primary antibody at a dilution of 1: 10 000 for 1h/RT with agitation in TBS with 2 % non-fat milk or ON/4°C with agitation. The antibody solution was decanted and the blot was rinsed briefly twice for 10 min. in TBS at RT with agitation. Blot was incubated in Agrisera matching secondary antibody (anti-rabbit IgG horse radish peroxidase conjugated, AS09 602) diluted to 1:75 000 in for 1h/RT with agitation. The blot was washed as above and developed using chemiluminescent detection. Exposure time was 26.5 seconds.
Courtesy of Dr. Christine Yao-Yun Chang and the Ensminger lab, University of Toronto, Canada

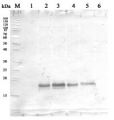
The detection of GS1 and GS2 proteins was performed using the crude extract of soluble proteins from Oryza sativa plants: Ref: Reference (control); D: Drought; CO2: High CO2 D+CO2: Drought + High CO2. Fresh leaves samples were ground until obtaining a fine powder in presence of liquid N2, ice-cold 100 mM K-phosphate buffer (pH 7.0) containing 1 mM EDTA and 2 mM ascorbic acid. After centrifugation at 14,000 x g for 30 min, the supernatant was collected and used as protein extract. All extraction stages were carried out at 4°C. The total soluble protein was measured according to the Bradford’s method. Leaf protein extracts were first separated by SDS-PAGE (Laemmli 1970). Equal amounts of protein (20 µg) were electrophoretically transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane (Towbin et al. 1979). Polypeptide detection was performed using specific polyclonal antibodies against GS1 and GS2 (AS08 295, Agrisera, Sweden). Membranes were blocked for 3 hours with 5% non-fat milk in saline Tris-HCl buffer (100 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.6, 150 mM NaCl), incubated with GS antibody overnight and after with alkaline phosphatase-conjugated secondary antibody by 6 hours. The protein detection was developed using NBT/BCIP (Sigma-Aldrich©, USA) by adding 1 tablet to 10 mL dH2O, until bands were visualized.
Courtesy of Dr. Ana Karla Lobo, Laboratory of Plant Metabolism, Federal University of Ceara, BrazilApplication examples: 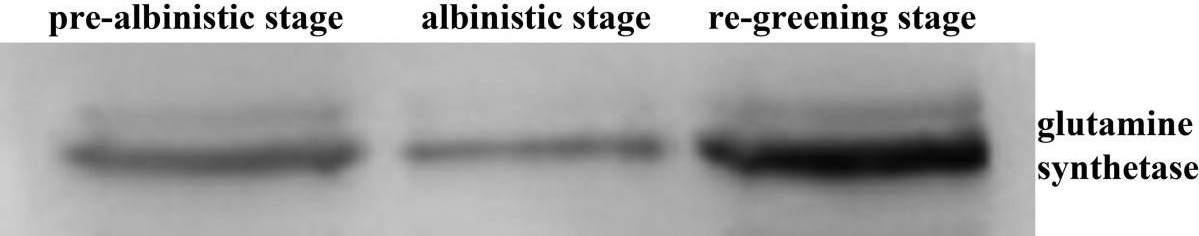
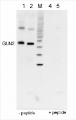
Reactant: Camellia sinensis (Tea plant)
Application: Western Blotting
Pudmed ID: 21806834
Journal: Proteome Sci
Figure Number: 5A
Published Date: 2011-08-02
First Author: Li, Q., Huang, J., et al.
Impact Factor: 2.037
Open PublicationWestern analysis of glutamine synthetase expression level at three developmental stages.
- Additional Information
-
Additional information: The antibody will recognize both, cytoplasmic and chloroplastic forms of the GS enzyme - Background
-
Background: Glutamine synthetase (GLN or GS) is one of the key enzymes involved in nitrogen metabolism of plants. It catalyses the synthesis of glutamine from glutamate and ammonia in an ATP-dependent reaction. There are two general classes of glutamine synthetase in plants: GLN1, a cytosolic form and GLN2, a chloroplastic form. GLN1 is highly abundant in the vascular elements of roots nodules, flowers and fruits, functioning in the assimilation of ammonium and the biosynthesis of glutamine for nitrogen transport. GLN2 is encoded by a single gene and is highly abundant in leaf mesophyll chloroplasts. Here GLN functions in the assimilation of ammonia produced from photorespiration and the reduction of nitrate in the chloroplasts
- Product Citations
-
Selected references: Souza et ak, (2025). The mitochondrial thioredoxin system regulates the TCA cycle-derived metabolic fluxes toward the GS/GOGAT cycle in illuminated leaves. J Exp Bot . 2025 Mar 24:eraf125. doi: 10.1093/jxb/eraf125.
Miyazawa et al. (2024). Photorespiratory metabolism differs between gymnosperm conifers and angiosperms. Journal of Forest Research, 1–10.
Rubio Wilhelmi et al. (2024). Salinity-Induced Photorespiration in Populus Vascular Tissues Facilitate Nitrogen Reallocation. Plant Cell Environ. 2024 Oct 1.doi: 10.1111/pce.15180.
Ding, Lv, Hu, et al. (2022) Phytosulfokine peptide optimizes plant growth and defense via glutamine synthetase GS2 phosphorylation in tomato [published online ahead of print, 2022 Dec 23]. EMBO J. 2022;e111858. doi:10.15252/embj.2022111858
Maresca et al. (2021) Biological responses to heavy metal stress in the moss Leptodictyum riparium (Hedw.) Warnst. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2022 Jan 1;229:113078. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.113078. Epub 2021 Dec 17. PMID: 34929502.
Silva et al. (2019). Characterization of plant glutamine synthetase S-nitrosation. Nitric Oxide. 2019 Apr 23;88:73-86. doi: 10.1016/j.niox.2019.04.006.
Wang et al. (2018). Response of Gracilaria lemaneiformis to nitrogen deprivation. Algal Research Volume 34, September 2018, Pages 82-96.
Witzel et al. (2017). Temporal impact of the vascular wilt pathogen Verticillium dahliae on tomato root proteome. J Proteomics. 2017 Oct 3;169:215-224. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2017.04.008.
Silva et al. (2015). Possible role of glutamine synthetase of the prokaryotic type (GSI-like) in nitrogen signaling in Medicago truncatula. Volume 240, November 2015, Pages 98–108.
Podgorska et al. (2013). Long-term ammonium nutrition of Arabidopsis increases the extrachloroplastic NAD(P)H/NAD(P)+ ratio and mitochondrial reactive oxygen species level in leaves but does not impair photosynthetic capacity. Plant Cell Environ. April 10.
Brouwer et al. (2011) TheImpact ofLightIntensity onShade-InducedLeaf Senescence. Plant Cell Environ. Dec. 15 (ahead of print).
Lang et al. (2011).Simultaneous isolation of pure and intact chloroplasts and mitochondria from moss as the basis for sub-cellular proteomics. Plant Cell Rep. 2011 Feb;30(2):205-15.doi: 10.1007/s00299-010-0935-4. - Protocols
-
Agrisera Western Blot protocol and video tutorials
Protocols to work with plant and algal protein extracts
Agrisera Educational Posters Collection
- Reviews:
-
Bastiaan Brouwer | 2009-03-19Very nice and strong antibody. Excellent to determine GS1/2 ratios in whole cell extracts.