1
Anti-ADH | Alcohol dehydrogenase (hypoxia marker)
AS10 685 | Clonality: Polyclonal | Host: Rabbit | Reactivity:Arabidopsis thaliana, Oryza sativa, Phaseolus vulgaris, Solanum lycopersicum
- Product Info
-
Immunogen: KLH-conjugated peptide derived from available ADH sequences including Arabidopsis thaliana P06525, At1g77120
Host: Rabbit Clonality: Polyclonal Purity: Serum Format: Lyophilized Quantity: 50 µl Reconstitution: For reconstitution add 50 µl of sterile water. Storage: Store lyophilized/reconstituted at -20°C; once reconstituted make aliquots to avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. Please remember to spin the tubes briefly prior to opening them to avoid any losses that might occur from material adhering to the cap or sides of the tube. Tested applications: Western blot (WB) Recommended dilution: 1 : 3000 (WB) Expected | apparent MW: 42 | 42 kDa (Arabidopsis thaliana)
- Reactivity
-
Confirmed reactivity: Arabidopsis thaliana, Fragaria vesca, Oryza sativa, Phaseolus vulgaris, Solanum lycopersicum
Predicted reactivity: Rorippa islandica
Species of your interest not listed? Contact usNot reactive in: Allyl alcohol dehydrogenase of Nicotiana tabacum, accession 75206691 and in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. - Application Examples
-
Application example

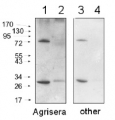
20 µg of total protein from Arabidopsis thaliana seedlings (0-4-8 hours of anoxic treatment with aerobic control) of WT Col-0 and adh mutant extracted with an SDS Extraction Buffer (60mM Tris-HCl pH 8.0, 2% SDS, 1,5% Sucrose) were separated on XT CRITERION 10%Bis-Tris (BioRad) SDS-PAGE and blotted 1h to PVDF. Blot was blocked immediately in milk in TBS-T for 1h at room temperature (RT) with agitation. Blot was incubated in the anti-ADH antibodies at a diluition of 1: 3000 in milk in TBS-T for 3h at RT with agitation. Blot was incubated in secondary antibody (goat anti-rabbit IgG HRP conjugated from Agrisera, AS09 602) diluited 1:20 000 in milk in TBS-T for 50 min at RT and then washed as above and developed for 2 min with chemiluminescent detection reagent. Images of the blot were obtained using BioSpectrum AC Imaging System (UVP). Exposure time was 10 min The arrow indicates ADH (42kDa, as expected) . There is a cross reacting band in Arabidopsis thaliana between 50-70 kDa. The large band in the right corner of the membrane is likely a staining artefact.

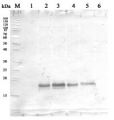
20 µg of total protein from Orysa sativa coleoptiles (3-4-5-6 days of germination under aerobic and anoxic conditions) extracted with an SDS Extraction Buffer (60mM Tris-HCl pH 8.0, 2% SDS, 1,5% Sucrose) were separated on XT CRITERION 10% Bis-Tris (BioRad) SDS-PAGE and blotted 1h to PVDF. The blot was blocked immediately in milk in TBS-T for 1h at room temperature (RT) with agitation. Blot was incubated in the anti-ADH antibodies at a diluition of 1: 3000 in milk in TBS-T for over night with agitation. Blot was incubated in secondary antibody (goat anti-rabbit IgG HRP conjugated from Agrisera, AS09 602) diluted 1:20 000 in milk in TBS-T for 50 min at RT and then washed as above and developed for 2 min with chemiluminescent detection reagent. Images of the blot were obtained using BioSpectrum AC Imaging System (UVP). Exposure time was 10 min. The band corresponds to ADH (41 kDa).
Courtesy Dr. Eleonora Paparelli,Scuola Superiore Sant'Anna, ItalyApplication examples: 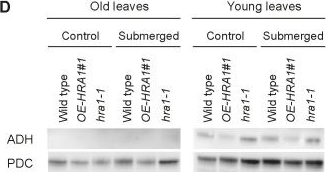
Reactant: Arabidopsis thaliana (Thale cress)
Application: Western Blotting
Pudmed ID: 25226037
Journal: PLoS Biol
Figure Number: 3D
Published Date: 2014-09-01
First Author: Giuntoli, B., Lee, S. C., et al.
Impact Factor: 7.279
Open PublicationHRA1 contributes to plant submergence survival.(A) Effect of HRA1 misexpression on rosette growth in air, or after recovery from 72 h submergence in darkness. Scale bar, 2 cm. (B) Percentage of plants surviving flooding-induced hypoxia (n?=?5), dry weight of rosette plants kept under control growth conditions (n?=?6), and dry weight of rosettes after postsubmergence recovery (n?=?6). Data are mean ± s.d.; *p<0.05, significant differences from the wild type after one-way ANOVA. (C) HRA1 regulates target gene transcripts in an age-dependent manner in leaves of plants treated with complete submergence. Transcripts were measured before submergence (“control conditions”), after 4 h submergence in darkness (“submergence”), and after 1 h de-submergence in the light (“reoxygenation”). Relative transcript values were calculated using old leaves of the wild type under control conditions as the reference sample. Data are mean ± s.d. (n?=?3); letters indicate statistically significant differences between genotypes after one-way ANOVA (p<0.05) performed independently on each leaf type. (D) Western blot analysis of ADH and PDC protein accumulation in leaves at different developmental stages from control and submerged (4 h) plants. The full-size images of the hybridized membranes can be found in Figure S10. (E) Stability of the translational fusion RAP2.12:RrLuc protein (RrLuc, Renilla reniformis luciferase) in Arabidopsis mesophyll protoplasts upon transfection with increasing amounts of 35S:HRA1. RAP2.12:RrLuc abundance was evaluated from the RrLuc relative activity, measured through a dual luciferase assay. Data are mean ± s.d. (n?=?4), and the asterisks indicate statistically significant differences (p<0.05) from protoplasts expressing RAP2.12:RrLuc alone, after one-way ANOVA.
Reactant: Arabidopsis thaliana (Thale cress)
Application: Western Blotting
Pudmed ID: 30861072
Journal: J Exp Bot
Figure Number: 6C
Published Date: 2019-03-27
First Author: Bui, L. T., Novi, G., et al.
Impact Factor: 6.088
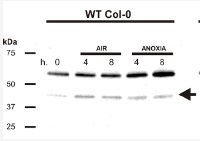
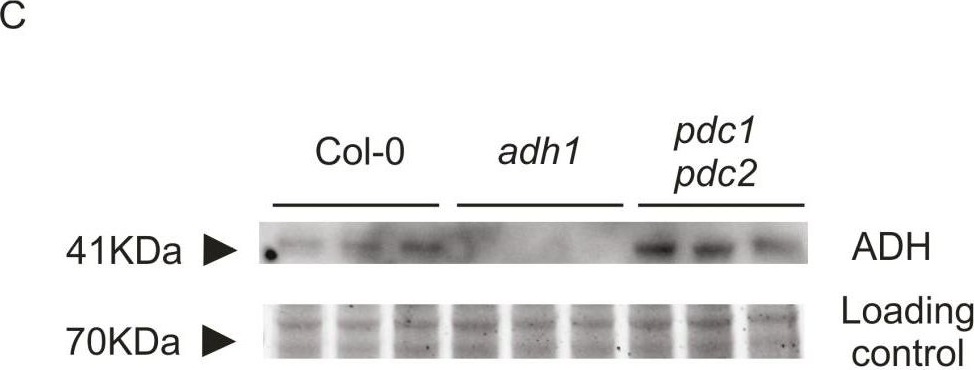
Open PublicationAssessment of ethanol fermentation in ADH and PDC mutants. (A) ADH activity in 6-day-old Arabidopsis seedlings (Col-0 wild type, and adh1, adh1adh2, and pdc1pdc2 mutants) after incubation under normoxic (21% O2 v/v) or hypoxic (1% O2 v/v) conditions for 12 h. The box plots are built on the bases of four replicates. (B) ADH1 expression in the wild type (Col-0), and adh1 and pdc1pdc2 mutants. The box plots are built on the bases of four replicates. (C) Immunodetection of ADH1 protein in aerobic wild-type (Col-0), adh1, and pdc1pdc2 seedlings, grown in liquid MS medium for 4 d, in the presence of 1% sucrose (w/v). Three biological replicates for each genotype are shown. Gel staining with Coomassie G-250 is shown as a protein loading control (D) Ethanol production in the same genotypes used for the ADH activity quantification shown in (A). The box plots are built on the bases of four replicates.
Reactant: Arabidopsis thaliana (Thale cress)
Application: Western Blotting
Pudmed ID: 32038671
Journal: Front Plant Sci
Figure Number: 6A
Published Date: 2020-02-11
First Author: Nibau, C., Gallemí, M., et al.
Impact Factor: 5.435
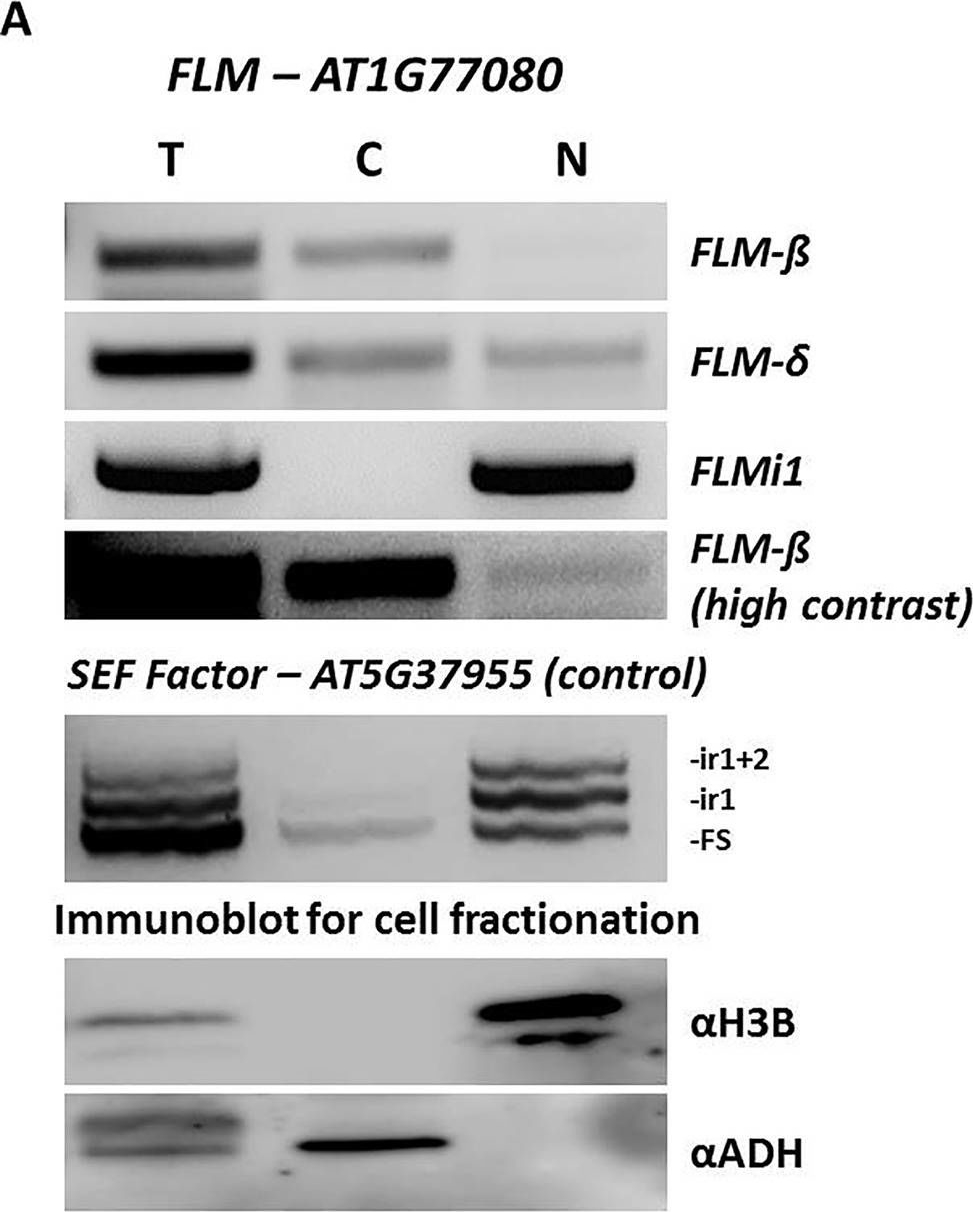
Open PublicationFLM intron 1 retention prevents nuclear export of FLM messenger RNA. (A) Expression analysis and sub-cellular localization of different FLM isoforms. Top panels, FLM-?, FLM-?, and FLMi1, in fractionated cell extracts (T-total, C-cytoplasmic, N-nuclear) by RT-PCR. FLM-? (high contrast) show nuclear localization for this isoform. Middle panel, The SEF factor splice variants in fractionated cell extracts. The SEF factor was used as a fractionation control as only the mature form (FS) is exported to the cytoplasm. FS, fully spliced; ir1, intron 1 retention; ir1+2, retention of introns 1 and 2. Lower panels, polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of protein extracts from the same cell fractionation. The cytoplasmic fraction is free of the nuclear protein histone 3B (H3B), and the nuclear fraction is free of the cytoplasmic alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH).
- Additional Information
-
Additional information: This product can be sold containing ProClin if requested - Background
-
Background: Alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) is an enzyme playing a crucial role in the fermentative metabolism in plants subjected to low oxygen stress. It is known to be synthesized preferentially under low oxygen conditions.
- Product Citations
-
Selected references: Zhang et al. (2024). BIG enhances Arg/N-degron pathway-mediated protein degradation to regulate Arabidopsis hypoxia responses and suberin deposition. Plant Cell. 2024 Apr 12:koae117. doi: 10.1093/plcell/koae117.
Czernicka et al. (2022). Proteomic Studies of Roots in Hypoxia-Sensitive and -Tolerant Tomato Accessions Reveal Candidate Proteins Associated with Stress Priming. Cells. 2022 Jan 31;11(3):500. doi: 10.3390/cells11030500. PMID: 35159309; PMCID: PMC8834170.
Ventura et al. (2020). Arabidopsis phenotyping reveals the importance of alcohol dehydrogenase and pyruvate decarboxylase for aerobic plant growth. Sci Rep. 2020 Oct 7;10(1):16669. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-73704-x. PMID: 33028901; PMCID: PMC7542448.
Gil-Monreal et al. (2019). ERF-VII transcription factors induce ethanol fermentation in response to amino acid biosynthesis-inhibiting herbicides. J Exp Bot. 2019 Aug 6. pii: erz355. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erz355.
Bui et al. (2019). Conservation of ethanol fermentation and its regulation in land plants. J Exp Bot. 2019 Feb 28. pii: erz052. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erz052.
De la Rosa et al. (2019), A dicistronic precursor encoding miR398 and the legume-specific miR2119 coregulates CSD1 and ADH1 mRNAs in response to water deficit. Plant Cell Environ. 2019 Jan;42(1):133-144. doi: 10.1111/pce.13209.
Giuntoli et al. (2014). A trihelix DNA binding protein counterbalances hypoxia-responsive transcriptional activation in Arabidopsis. PLoS Biol. 2014 Sep 16;12(9):e1001950. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001950. eCollection 2014. - Protocols
-
Agrisera Western Blot protocol and video tutorials
Protocols to work with plant and algal protein extracts
Agrisera Educational Posters Collection
- Reviews:
-
Mirko Zaffagnini | 2020-01-28The antibody reacts with recombinant ADH from Arabidopsis thaliana displaying no reactivity towards ADH2/GSNOR. In addition, it nicely detects ADH from Arabidopsis protein extracts showing a single band.