Secondary antibody guide
Recommended Agrisera secondary antibodies
Based on an analysis of antibody performance in available publications, conducted by CiteAB, it is clear that Agrisera's secondary antibodies perform above market average. This means that Agrisera secondary antibodies can be used at high dilutions, and are therefore price-worthy reagents, that will provide you with a consistent performance over many experiments.
Clearing up some terminology
- Goat: The first part of the name of any of our secondary antibodies lets you know the host species. In this example, the antibody was produced in Goat.
- anti-Rabbit IgG: The second part of the name tells you that the antibody was made to Rabbit IgG, and thus specifically binds to this molecule. This means that it can be used with any primary antibody made in Rabbit. Detailed information on different types of immunoglobulins can be found under Antibody types on our page Protocols and Technical information.
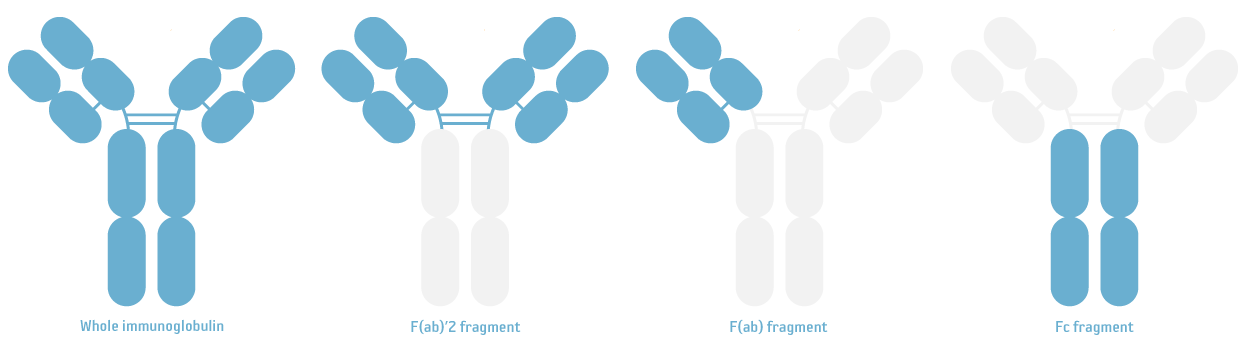
- (H&L): This part denotes that the secondary antibody will recognize both the Heavy & Light chain of Rabbit IgG. IgG molecules are comprised of two identical heavy chains, and two identical light chains. Both the heavy and light chains are further categorized into constant and variable parts, but H&L refers to the complete chains, i.e. the whole immunoglobulin.
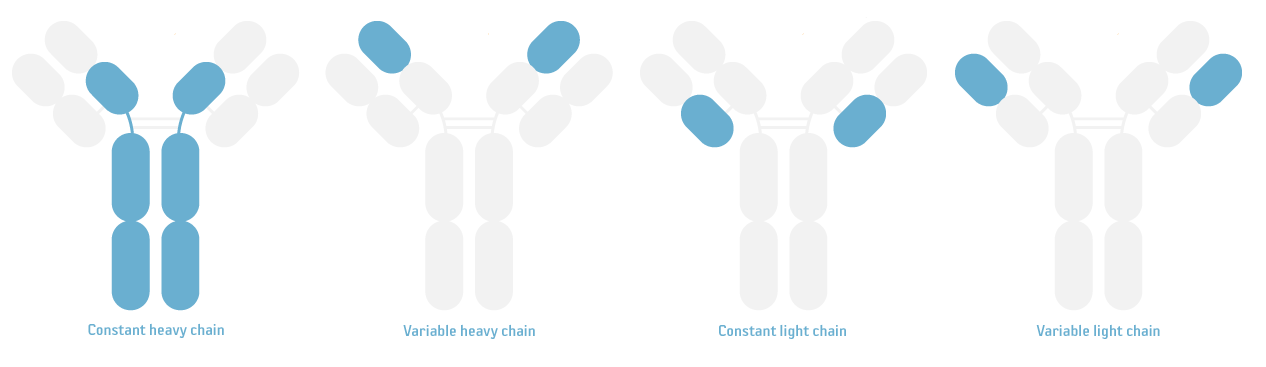 Image 1. Depiction of an immunoglobulin molecule with the constant heavy chains, variable heavy chains, constant light chains and variable light chains highlighted.
Image 1. Depiction of an immunoglobulin molecule with the constant heavy chains, variable heavy chains, constant light chains and variable light chains highlighted.
- HRP-conjugated: The last part of the name in this example tells you that the antibody is conjugated to Horseradish Peroxidase (HRP). For more details on different conjugations, see the conjugations section below.
Conjugations
- HRP: Horseradish peroxidase (HRP) catalyzes the oxidation of specific substrates, which gives rise to a characteristic color change or the emission of light. When using secondary antibodies conjugated to HRP, the detection is thus chromogenic, chemiluminescent or fluorescent, and can be observed by the naked eye, or recorded by a CCD camera. This type of conjugate is characterized by long shelf-life and good stability.
- ALP: Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of phosphate esters at alkaline pH, producing a colored or fluorescent product. When using antibodies conjugated to ALP, visualization of the antibody binding to the target is often achieved using chromogenic reagents, and no CCD camera is necessary. An ALP-conjugated secondary antibody is thus a good choice when there is no CCD camera available in the lab. Visualization is also possible using chemiluminescence, with high sensitivity. ALP detection may offer low background signal for certain types of samples or assay conditions.
- Biotin: Biotin, also known as Vitamin B7 or Vitamin H, is a small molecule with high affinity to avidin and streptavidin. Biotin-streptavidin is one of the strongest non-covalent interactions in nature, and the binding is nearly irreversible, allowing the formation of extremely stable complexes, resistant to denaturation by heat, pH and other denaturing agents. Biotin-conjugated (or biotinylated) secondary antibodies are often used when the target protein is of low expression. This is due to the fact that the signal is amplified, as multiple biotin molecules will bind to a single IgG molecule. For detection in immunoassays, the biotin-conjugated antibody is utilized together with avidin or streptavidin, coupled to HRP, ALP or a fluorescent dye.
- Dylight®: Dylight® is a group of fluorescent dyes with high fluorescence intensity and photostability. Agrisera offers secondary antibodies conjugated to these fluorophores, with absorption at 350, 405, 488, 550, 594, 633, 650, 680 and 800 nm. These wavelengths have low spectral overlap, which means that they can be combined to produce multi-color imaging.
 Image 2. Visible light spectrum with Dylight® wavelengths marked out.
Image 2. Visible light spectrum with Dylight® wavelengths marked out.
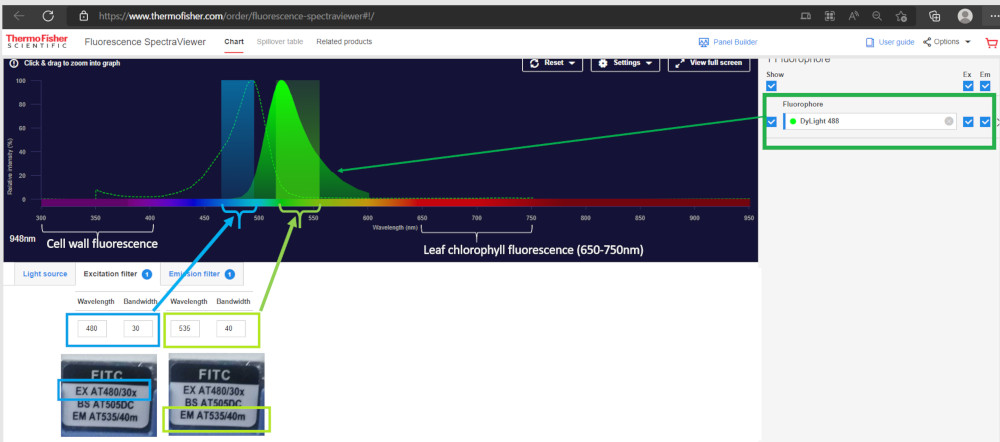
Dylight® 488 is recommended for immunofluorescence in plant tissues. Using this wavelength will allow the exclusion of cell wall autofluorescence and chlorophyll fluorescence (range of 640-850 nm, with two peaks at 690 nm and 740 nm).
- FITC: Fluorescein Isothiocyanate (FITC) is a fluorophore that absorbs ultraviolet or blue light with absorption at 488 nm, excitation at 498 nm, and emission at 517 nm. This is one of the most commonly used fluorescent dyes, and due to this, the majority of instruments come with 488 nm laser as the standard. FITC is compatible with a range of imagining techniques, for specific labeling of target molecules, and their visualization and tracking in structures within cells and tissue.
- TRITC: Tetramethylrhodamine (TRITC) is a red-orange fluorophore with adsorption at 532 nm, excitation at 557 nm, and emission at 576 nm. TRITC is widely used in immunofluorescence staining, for labelling specific proteins and structures within cells, as well as in fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH), to visualize specific nucleic acid sequences. TRITC has moderate photostability.
- Unconjugated: Unconjugated antibodies have not been labeled with any type of reporter molecule, like a dye or an enzyme, and can be used as capture or detection antibodies in immunoassays, such as ELISA or Immunofluorescence assay (IFA). Such antibodies are also employed in Immunoprecipitation (IP) and flow cytometry (Flowcyt) for cell surface or intracellular staining, to identify and quantify specific cell populations based on their surface markers or intracellular proteins. Beyond this, they can also be used when you wish to choose the conjugation yourself. This may be a good option when doing complex Flowcyt or Multiplex assays.
| Conjugation | Laser lane | Common filter | Ex/em max | Spectrally similar dyes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 355 | 450/50 nm | 353/432 nm | Alexa Fluor 350, AMCA | |
| 488 | 525/50 nm | 493/518 nm | Alexa Fluor 488, fluorescein, FITC | |
| 488 | 530/43 nm | 497/517 nm | Dylight® 488, Alexa Fluor 488, fluorescein | |
| 532 | 585/42 nm | 557/576 nm | Dylight® 550, Alexa Fluor 546, Alexa Fluor 555, Cy3 | |
| 561 | 585/42 nm | 562/576 nm | Alexa Fluor 546, Alexa Fluor 555, Cy3, TRITC | |
| 594 | 630/69 nm | 593/618 nm | Alexa Fluor 594, Texas Red | |
| 628-640 | 660/20 nm | 638/658 nm | Alexa Fluor 633 | |
| 628-640 | 695/40 nm | 652/672 nm | Alexa Fluor 647, Cy5 | |
| 628-640 | 695/40 nm | 692/712 nm | Alexa Fluor 680, Cy5.5 | |
| 785 | 780/60 nm | 777/794 nm | IRDye 800 |
Some more antibody terms
- Min. cross-reactivity: Minimal cross-reactivity means that the secondary antibody will not recognize other types of immunoglobulins than the one it is targeted for. For example, Goat anti-Human IgM, min. cross-reactivity to human IgG and IgA denotes that the secondary antibody is specific to Human IgM, and will not bind to Human IgG or IgA, as there is minimal cross-reactivity to these other immunoglobulins.
- Pre-adsorbed: Also called cross-adsorption, and often used synonymously with minimal cross-reactivity. Pre-adsorption is a purification step, during which the secondary antibody solution is passed through a column, with serum proteins of potentially cross-reactive species immobilized in the matrix. The specific antibodies pass through the column, and constitute the purified product, while the non-specific ones bind to the serum proteins in the column and are later discarded.
- F(ab)'2 fragment: The F(ab)'2 fragment of an antibody consists of just the two ligh chain dimers, linked together by a disulfade bond to preserve the antigen-binding site. In this case, the Fc part of the antibody has thus been removed, which prevents non-specific binding to cell Fc receptors and Protein A/G. This type of secondary antibody is used in very specific applications, involving whole mammalian cells or tissue samples, as they can penetrate the tissue easier and eliminates cross-reactions to Fc receptors.
- Fc fragment: The Fc fragment of an antibody consists only of the lower part of the heavy chains. Secondary antibodies produced against the Fc part of another species, will thus only interact with the heavy chain of the target antibody.
FAQ
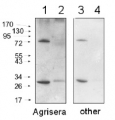
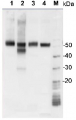
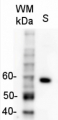
| No. Secondary antibodies most importantly differ in respect to dillution they can be applied at. |
| A matching secondary antibody, that can be used at high dilutions, will contribute to good Western blot results, with less risk for background signal. Beyond this, it can be used for many experiments, and is therefore very cost-efficient. The differences between secondary antibodies from various suppliers are discussed here. Agrisera's primary antibodies are produced in chicken, goat, mouse, rabbit and rat. The following high-titer secondary antibodies are appropriate matches:
*This antibody is in the group of the most published antibodies in the world, based on publication record analyses performed by CiteAB. |
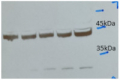
Therefore, if the protein you aim to detect in Western blot, following immunoprecipitation with an antibody, has a molecular weight of ~50 kDa, an anti-Rabbit light chain-specific antibody should be used.
If the protein of interest is ~25 kDa, an anti-rabbit IgG Fc specific antibody shoule be used, such as Goat anti-Rabbit IgG Fc, HRP conjugated, min. cross-reactivity to bovine horse or human serum proteins.
ECFP (EX at 435/20x), (Beam Splitter at 455DC), (EM at 535/40m)
FITC (EX at 480/30x), (Beam Splitter at 505DC), (EM at 535/40m)
TRITC (EX at 540/25x), (Beam Splitter at 565DC), (EM at 605/55m)
Which DyLight®-conjugated secondary antibody can be recommended?
DyLight® 488 conjugated secondary antibodies are recommended with FITC filter, as this will not interfere neither with the cell wall autofluorescence, nor with the chlorophyll fluorescence. See image below, which is a compilation from ThermoFisher Fluorescence SpectraViewer.
| CCD cameras are often used for visualizing the binding of an antibody to a target protein, through chemiluminescent or fluorescent detection. In cases where a CCD camera is not available in the laboratory, secondary antibodies conjugated to alkaline phosphatase (ALP) can be used, and the reaction can instead be visualized using Agrisera TMB reagents. This way, medium and high abundancy proteins can be visualized easily, and the obtained results can be saved in the lab book (although please remember that there is a fading effect). |
Agrisera offers a wide range of high-titer secondary antibodies, for detection of primary antibodies from different hosts, like goat, llama, mouse, rabbit, rat and many more.
Our secondary antibodies have the following features:
- High sensitivity
- High average dilution
- Long-term stability
- Superior lot-to-lot consistency
- Most of Agrisera's primary antibodies were validated in pair with our secondary antibodies
This means that we can offer you a working antibody pair to secure success of your Western blot experiment.
Check out the complete collection of Agrisera secondary antibodies